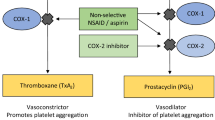
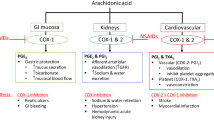
Summary
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are widely used for the relief of the symptoms of osteoarthritis (OA), rheumatoid arthritis (RA), sprains and strains, sports injuries and menstrual disorders, and have a small role in the management of patent ductus arteriosus in the neonate.
In patients with RA, symptom relief through use of NSAIDs is firmly established, although it remains unclear whether they influence the course and outcome of the disease. For the average patient with RA taking NSAIDs, the attributable risk of hospitalisation with gastrointestinal problems related to NSAIDs is 1.3 to 1.6% annually and risk of death is 0.15%. Associations of therapy with risk are greatest with age, corticosteroid use and previous NSAID-related gastrointestinal adverse effects, and less marked with disability and high NSAID dose. These are important data in attempting to balance risk of therapy with clinical efficacy in an individual patient, and assessing the cost-effectiveness of prophylaxis.
Although half of all NSAID consumption is for control of pain associated with degenerative conditions, their superiority over simple analgesics in osteoarthritis is poorly documented. This finding supports the use of the simple analgesic paracetamol (acetaminophen) as the preferred therapy of osteoarthritis, especially when its lower cost and low incidence of adverse effects are taken into consideration.
Consistent differences in clinical effectiveness of individual NSAIDs have not been demonstrated, although unpredictable interpatient variation in response to individual agents is of considerable clinical importance, and a more expensive NSAID may prove cost effective for some patients. Cost effectiveness can be improved by a self-adjusted dosage regime which also leads to lower overall drug consumption. The adverse gastrointestinal effects of these drugs account for about 30% of the overall cost of arthritis treatment, and although studies to date have been too limited to assess the relative risk of gastrointestinal toxicity of the different NSAIDs reliably, ibuprofen appears to be one of the least hazardous, and azapropazone one of the most hazardous. Although the effectiveness of prophylaxis with H2-antagonists and with prostaglandin Ei analogues (prostaglandin-E1 analogues has been established, estimates of cost-benefit ratios are widely divergent. To establish the most cost-effective therapy with NSAIDs, more data are required to establish multivariable risk profiles for identification of patients at particular risk, the optimal drug, and its optimal dosage and duration of treatment. A more cost-effective use of NSAIDs could be achieved by a more thorough clinical assessment of efficacy in an individual patient which would lead to a lower overall use but greater therapeutic benefit.
There is only limited evidence for the efficacy of NSAIDs in acute musculoskeletal disorders such as strains, sprains or sports injuries. There is no clear evidence of superiority among drugs, and no studies have yet examined the pharmacoeconomic aspects of their use compared with other effective treatment options.
Although satisfactory cost-effectiveness data are not available for the use of NSAIDs in management of dysmenorrhoea, they are clinically effective (particularly ibuprofen, naproxen and mefenamic acid), and serious adverse effects are rare because of the short treatment periods. NSAIDs have limited efficacy in reducing blood loss in menorrhagia, and there is no clear evidence of superiority among agents. Pharmacoeconomic studies to support their cost effectiveness over other treatment options are not available.
Indomethacin has a role as a preferred and cost-effective treatment for patent ductus arteriosus in the neonate, with surgery being used when drug therapy fails.
Only limited data on the cost effectiveness of NSAIDs are available, despite their wide use. In part, this reflects the primarily clinical assessment of the effectiveness of treatments. The development of standardised and well validated assessment instruments is required. Such data as are available are sometimes from poorly designed studies. Future studies must include randomisation of treatments and blinding of participants to therapies wherever possible.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aadland E, Fausa O, Vahn M, Cohen H, Quinlan D. Protection by misoprostol against naproxen-induced gastric mucosal damage. American Journal of Medicine 83: 37–40, 1987
Akermark C, Forsskahl B. Topical indomethacin in overuse injuries in athletes. A randomized double-blind study comparing elmetacin with oral indomethacin and placebo. International Journal of Sports Medicine 11: 393–396, 1990
Anderson JJ, Felson DT, Meenan RB, Williams HJ. Which traditional measures should be used in rheumatoid arthritis clinical trials? Arthritis and Rheumatism 32: 1093–1099, 1989
Anderson R-B, Needlemam RD, Gatter RA, Andrews RP, Scarola JA. Patient outcome following inpatient YS outpatient treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Journal of Rheumatology 15: 556–560, 1988
Andersson S, Fredin H, Lindberg H, Sanzen L, Westlin N. Ibuprofen and compression bandage in the treatment of ankle sprains. Acta Orthopaedica Scandinavica 54: 322–325, 1983
Anon. Diclofenac gel — topical NSAIDs and science. Drugs and Therapeutics Bulletin 24: 95–96, 1991
Barradell LB, Whittington R, Benfield P. Misoprostol: pharmacoeconomics of its use as prophylaxis against gastroduodenal damage induced by nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. PharmacoEconomics 3: 140–170, 1993
Bergsjo P, Jenssen H, Vellar OD. Dysmenorrhea in industrial workers. Acta Obstetrica Gynecologica Scandinavica 54: 255–259, 1975
Bloom BS. Direct medical costs of disease and gastrointestinal side effects during treatment for arthritis. American Journal of Medicine 84: 20–24, 1988
Borg G, Allander E, Goobar JE. Disease-modifying antirheumatic drug therapy. Scandinavian Journal of Rheumatology 19: 115–121, 1990
Bradley JD, Brandt KD, Katz BP, Kalasinska LA, Ryan SI. Comparison of an antiinflammatory dose of ibuprofen, an analgesic dose of ibuprofen, and acetaminophen in the treatment of patients with osteoarthritis of the knee. New England Journal of Medicine 325: 87–91, 1991
Brooks PM, Dougan MA, Mugford S, Meffn E. Comparative effectiveness of 5 analgesics in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis. Journal of Rheumatology 9: 723–726, 1982
Capell HA, Rennie JAN, Rooney PJ, Murdoch RM, Hole DJ, et al. Patient compliance: a novel method of testing non-steroidal anti-inflammatory analgesics in rheumatoid arthritis. Journal of Rheumatology 6: 584–592, 1979
Carne P. Nonsurgical treatment of ankle sprains using the modified Sarmiento brace. American Journal of Sports Medicine 17: 253–257, 1989
Carrin GJ, Torfs KE. Economic evaluation of prophylactic treatment with misoprostol in osteoarthritic patients treated with NSAIDs. The case of Belgium. Revue d’Epidemiologie et de Sante Publique 38: 187–199, 1990
Cholst IN, Carlon AT. Oral Contraceptives and Dysmenorrhea. Journal of Adolescent Health Care 8: 121–128, 1987
Clyman RI, Campbell D. Indomethacin therapy for patent ductus arteriosus: when is prophylaxis not prophylactic? Journal of Pediatrics 111: 718–721, 1987
Coke H. Long term indomethacin treatment for coxarthrosis. Annals of Rheumatic Disease 26: 346–347, 1967
Committee on Safety of Medicines update. Non-steroidal antiinflammatory drugs and serious intestinal adverse reactions — 2. British Medical Journal 292: 1190–1191, 1986
Dawood MY. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and changing attitudes towards dysmenorrhea. Americal Journal of Medicine 84: 23–29, 1988
Day RO, Graham GG, Williams KM, Brookes PM. Variability in response to NSAIDs: fact or fiction? Drugs 36: 643–651, 1988
de Loes M. Medical treatment and costs of sports-related injuries in a total population. International Journal of Sports Medicine 11: 66–72, 1990
Diebschlag W, Nocker W, Bullingham R. A double-blind study of the efficacy of topical ketorolac tromethamine gel in the treatment of ankle sprain, in comparison to placebo and etofenamate. Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 30: 82–89, 1990
Dieppe P, Cushnaghan J, Jasani K, McCrae F, Watt I. A two-year placebo controlled trial of a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory (NSAID) in knee osteoarthritis (OA). British Journal of Rheumatology 29: 129, 1990
Dockeray CJ, Sheppard BL, Bonnar J. Comparison between mefenamic acid and danazol in the treatment of established menorrhagia. British Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology 96: 840–844, 1989
Downie WW, Prostaglandins and NSAID in the kidney. Journal of Rheumatology 18: 19–21, 1991
Doyle DV, Dieppe PA, Scott J, Huskisson EC. An articular index for the assessment of osteoarthritis. Annals of Rheumatic Diseases 40: 75–78, 1981
Ehsanullah RSB, Page MC, Tildesley G, Wood JR. Prevention of gastroduodenal damage induced by non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: controlled trial of ranitidine. British Medical Journal 297: 1017–1021, 1988
Felson DT, Anderson JJ, Meenan RF. The comparative efficacy and toxicity of second-time drugs in rheumatoid arthritis: results of two meta-analyses. Arthritis and Rheumatism 33: 1449–1461, 1990
Felson DT, Anderson JJ, Nalmark A, Kannel W, Meenan RF. The prevalence of chondrocalcinosis in the elderly and its association with knee osteoarthritis: the Framingham study. Journal of Rheumatology 16: 1241–1245, 1990
Frank GJ, Kefford RH. Report of a double-blind crossover study to compare flurbiprofen with paracetamol in the treatment of primary dysmenorrhoea. Journal of International Medical Research 11 (Suppl. 2): 6–10, 1983
Fraser IS, McCarron M. In Lewis TLT & Chamberlain GVP (Eds) Gynaecology by ten teachers, 15th ed., pp. 174–181, Edward Arnold, London, 1991
Friedman DM, Moore ME. The efficacy of intraarticular steroids in osteoarthritis: a double-blind study. Journal of Rheumatology 7: 850–856, 1980
Fries JF. Postmarketing drug surveillance: are our priorities right? Journal of Rheumatology 15: 389–390, 1988
Fries JF. NSAID gastropathy: the second most deadly rheumatic disease? Epidemiology and risk appraisal. Journal of Rheumatology 18: 6–10, 1991
Furniss LD. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agents in the treatment of primary dysmenorrhea. Clinical Pharmacy 1: 327–333, 1982
Gannon MJ, Holt EM, Fairbank J, Fitzgerald M, Milne MA, et al. A randomised trial comparing endometrial resection and abdominal hysterectomy for the treatment of menorrhagia. British Medical Journal 303: 1362–1364, 1991
Geis GS, Suad H, Wallemark C-B, Nicholson PA. Prevalence of mucosal lesions in the stomach and duodenum due to chronic use of NSAID in patients with rheumatoid or osteoarthritis and interim report on prevention by misoprostol of diclofenac associated lesions. Journal of Rheumatology 18: 11–14, 1991
Gersony WM. Patent ductus arteriosus in the neonate 33: 545–560, 1986
Gibson T. Sports injuries. Bailliere’s clinical rheumatology 1: 583–600, 1987
Graham DY, Agrawal NM, Ro-m SH. Prevention of NSAlD-induced gastric ulcer with the synthetic prostaglandin, misoprostol: a multicenter, double-blind, placebo controlled trial. Lancet 2: 1277–1280, 1988
Gray RG, Tenenbaum J, Gottlieb NL. Local corticosteroid injection treatment in rheumatic disorders. Seminars in Arthritis and Rheumatism 10: 231–254, 1981
Griffin JP, Weber JCP. Adverse drug reactions and acute poisoning reviews 4: 213–130, 1985
Griffin MR, Ray WA, Schaffner W. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug use and death from peptic ulcer in elderly persons. Annals of Internal Medicine 109: 359–363, 1988
Guyer B, Ellers B. Childhood injuries in the United States. American Journal of Diseases of Children 144: 649–652, 1990
Hanson FW, Inzu A, Hennzl MR. Naproxen sodium in dysmenorrhea, its influence in allowing continuation of work/school activities. Obstetrics and Gynaecology 52: 583–587, 1978
Hawkey CJ. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and peptic ulcers. British Medical Journal 30: 278–284, 1990
Helewa A, Bombardier C, Goldsmith CH, Menchions B, Smythe HA. Cost-effectiveness of inpatient and intensive outpatient treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis and Rheumatism 32: 1505–1514, 1989
Higham JM. The medical management of menorrhagia. British Journal of Hospital Medicine 45: 19–22, 1991
Higham JM, Shaw RW. Risk-benefit assessment of drugs used for the treatment of menstrual disorders. Drug Safety 6: 183–191, 1991
Hillman AL, Bloom BS. Economic effects of prophylactic use of misoprostol to prevent gastric ulcer in patients taking nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Archives of Internal Medicine 149: 2061–2065, 1989
Honig S. Clinical trials in acute musculoskeletal injury states. American Journal of Medicine 84: 42–55, 1988
Jacobs J, Keyserling JA, Britton M, Morgan GJ, Wilkenford J, et al. The total cost of care and the use of pharmaceuticals in the management of rheumatoid arthritis: the medical program. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 41: 215–223, 1988
Janbu T, Lokken P, Nesheim B-I. Effect of acetylsalicylic acid, paracetamol, and placebo on pain and blood loss in dysmenorrhoeic women. European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 14: 413–416, 1978
Jefferson TO. An investigation of medical discharges from the British army 1979–1986. Journal of the Royal Army Medical Corps 135: 115–123, 1989
Jenner PN. Nabumetone in the treatment of skin and soft tissue injury. American Journal of Medicine 83: 101–106, 1987
Johnson MR, Schultz MK, Ferguson AC. A comparison of chiropractic, medical and osteopathic care for work-related sprains and strains. Journal of Manipulative and Physiological Therapeutics 12: 335–344, 1989
Jonsson B, Larsson S-E. Functional improvement and costs of hip and knee arthroplasty in destructive rheumatoid arthritis. Scandinavian Journal of Rheumatology 20: 351–357, 1991
Keagy RD, Keim HA. Intra-articular steroid therapy: repeated use in patients with chronic arthritis. American Journal of Medical Sciences 253: 45–51, 1967
Kjaersgaard-Anderson P, Nafei A, Skor O, Madsen F, Andersen HM, et al. Codeine plus paracetamol versus paracetamol in longer-term treatment of chronic pain due to osteoarthritis of the hip. A randomised, double-blind, multicentre study. Pain 43: 309–318, 1990
Knill-Jones R, Drummond M, Kohli H, Davies L. Economic evaluation of gastric acid prophylaxis in patients with arthritis receiving non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Postgraduate Journal 66: 639–646, 1990
Krishnan G. A placebo-controlled, double-blind trial of benorylate tablets in the treatment of bursitis and synovitis due to sports injury. Rheumatology and Rehabilitation 16: 186–189, 1977
Kvien TK, Brors O, Staff PH, Rognstad S, Norby J. Improved cost-effectiveness ratio with a patient self-adjusted naproxen dosing regimen in osteoarthritis treatment. Scandinavian Journal of Rheumatology 20: 280–287, 1991
Lahteenmaki P. Management of menorrhagia. British Medical Journal 301: 290–291, 1990
Langmam MJS. Ulcer complications and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. American Journal of Medicine 86: 15–19, 1988
Laporte JR, Carne X, Vidal X. Upper gastrointestinal bleeding in relation to previous use of analgesics and non-steroidal antiinflammatory drugs. Lancet 337: 85–89, 1991
Lee P, Kennedy AC, Anderson J, Buchanan WW. Benefits of hospitalization in rheumatoid arthritis. Quarterly Journal of Medicine 43: 205–214, 1974
Levy RA, Smith DL. Clinical differences among non-steroidal antiinflammatory drugs: implications for therapeutic substitution in ambulatory patients. Annals of Pharmacotherapy 23: 76–78, 1989
Liang MH, Cullen KE, Larson MG, Thompson MS, Schwartz JA, et al. Cost effectiveness of total joint arthroplasty in osteoarthritis. Arthritis and Rheumatism 29: 937–943, 1986
Liang MH, Daltrey LH. The impact of inflammatory arthritis on society and the individual options for public health programs. In Hadler & Gillings (Eds) Arthritis and society, pp 3–16, Butterworths, London, 1985
Liang MH, Larson M, Thompson M, Eaton H, McNamara E, et al. Costs and outcomes in rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis. Arthritis and Rheumatism 27: 522–529, 1984
Lubeck DP, Spitz PW, Fries JF, Wolfe F, Mitchell DM, et al. A multicenter study of annual health service utilization and cost in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis and Rheumatism 29: 488–493, 1986
McDuffie FC. The cost of treating arthritis. Hospital Therapy (Suppl.): 12–23, 1986 Mcllwain, HH
Piatt RD. Piroxicam Yersus Naproxen in the treatment of acute musculoskeletal disorders in athletes. American Journal of Medicine 84: 56–60, 1988
Magos AL. Management of menorrhagia. British Medical Journal 300: 1537–1538, 1990
Meenan RF, Yelin EH, Henke CJ, Curtis DL, Epstein WW. The costs of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis and Rheumatism 21: 827–833, 1978
Milsom I, Andersch B. Effect of ibuprofen, naproxen sodium and paracetamol on intrauterine pressure and menstrual pain in dysmenorrhoea. British Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology 91: 1129–1135, 1984
Milsom I, Sundell G, Andersch B. The influence of different combined oral contraceptives on the prevalence and severity of dysmenorrhea. Contraception 42: 497–507, 1990
Nabrink M, Birgersson L, Colling-Saltin A-S, Solum T. Modern oral contraceptives and dysmenorrhoea. Contraception 42: 275–283, 1990
Nilsson L, Rybo G. Treatment of menorrhagia. Americal Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology 110: 713–720, 1971
Owen PR. Prostaglandin synthetase inhibitors in the treatment of primary dysmenorrhea. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology 148: 96–103, 1984
Parniapour M, Nordin M, Skovron ML, Frankel VH. Environmentally induced disorders of the musculoskeletal system. Medical Clinics of North America 74: 347–359, 1990
Parr G, Darekar B, Fletcher A, Bulpitt CJ. Joint pain and quafitV of life; results of a randomised trial. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 27: 235–242, 1985
Pelletier JP, 2 Martel-Pelletier J. Protective effects of corticosteroids on cartage lesions and osteophyte formations in the Pond-Nuki dog model of osteoarthritis. Arthritis and Rheumatism 32: 181–193, 1989
Pullar T, Capell HA, Millar A, Brooks RG. Alternative medicine: cost and subjective benefit in rheumatoid arthritis. British Medical Journal 285: 1629–1631, 1982
Rashad S, Revell P, Hemingway A, Low F, Rainsford K, et al. Effect of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs on the course of osteoarthritis. Lancet ii: 519–522, 1989
Rees M. Menorrhagia. British Medical Journal 294: 759–762, 1987
Rempel DM, Harrison RJ, Barnhart S. Work-related cumulative trauma disorders of the upper extremity. Journal of the American Medical Association 267: 838–842, 1992
Roth SH, Bennett RE, Mitchel CS, Hartman RJ. Cimetidine therapy in nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug gastropathy. Double-blind long term evaluation. Archives of Internal Medicine 147: 1798–1801, 1987
Royal College of General Practitioners, Office of Population Census Statistics, Department of Health and Social Security. Morbidity statistics from general practice 1981–82, HMSO Series MBS No. 1, London 1986
Rutherford AJ, Glass M R. Management of menorrhagia. British Medical Journal 301: 290–291, 1990
Ruwe PA, Wright J, Ramdall RL, Lynch JK, Jokl P, et al. Can MR imaging effectively replace diagnostic arthroscopy? Radiology 183: 335–339, 1992
Scott DL, Dacre JE, Greenwood A, Treasure L, Huskisson EC. Can we develop simple response criteria for slow acting antirheumatic drugs? Annals of Rheumatic Disease 49: 196–198, 1990
Shapiro SS. Treatment of dysmenorrhoea and premenstrual syndrome with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Drugs 36: 475–490, 1988
Shenassa H, Sankaran K, Duncan W, Tyrrell M, Bharadwa B. Surgical litigation of patent ductus arteriosus in a neonatal intensive care setting is safe and cost effective. Canadian Journal of Cardiology 2: 353–355, 1986
Singh G, Fries JF, Williams CA. Toxicity profiles of disease modifying antirheumatic drugs in rheumatoid arthritis. Journal of Rheumatology 18: 188–194, 1991
Smith RP, Powell JR. The objective evaluation of dysmenorrhea therapy. Americal Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology 137: 314–319, 1980
Soboroff SH, Pappius EM, Komaroff AL. Benefits, risks, and costs of alternative approaches to the evaluation and treatment of severe ankle sprain. Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research 183: 160–167, 1984
Somerville K, Faulkner G, Langman M. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and bleeding peptic ulcer. Lancet 1: 462–464, 1986
Stone CE. The lifetime economic costs of rheumatoid arthritis. Journal of Rheumatology 11: 819–827, 1984
Tucker M, Kirwan JR. Does patient education in rheumatoid arthritis have therapeutic potential? Annals of Rheumatic Diseases 50: 422–428, 1991
Valtonen EJ. Clinical comparison of triamcinolone-hexacetonide and betatmethasone un the treatment of osteoarthrosis of the knee joint. Scandinavian Journal of Rheumatology 41 (Suppl.): 1–7, 1981
Wenzloff NJ, Shimp L. Therapeutic management of primary dysmenorrhea. Drug Intelligence and Clinical Pharmacy 18: 22–26, 1984
Wills CA, Washburn S, Caiozzo, Prietto CA. Achilles tendon rupture. Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research 207: 156–163, 1986
Wolfe F, Kleinheksel SM, Spitz PW, Lubeck DP, Fries JF, et al. A multicenter study of hospitalization in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis and Rheumatism 29: 614–619, 1986
Ylikorkala O, Viinikka L. Comparison between antibifrinolytic and antiprostaglandin treatment in the reduction of increased menstrual blood loss in women with intrauterine contraceptive devices. British Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology 90: 78–83, 1983
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wynne, H.A., Campbell, M. Pharmacoeconomics of Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs). Pharmacoeconomics 3, 107–123 (1993). https://doi.org/10.2165/00019053-199303020-00004
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2165/00019053-199303020-00004