Abstract
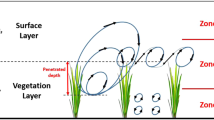
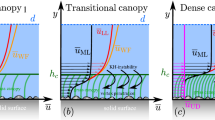
This paper reviews recent work on flow and transport in channels with submerged vegetation, including discussions of turbulence structure, mean velocity profiles, and dispersion. For submerged canopies of sufficient density, the dominant characteristic of the flow is the generation of a shear-layer at the top of the canopy. The shear-layer generates coherent vortices by Kelvin-Helmholtz (KH) instability. These vortices control the vertical exchange of mass and momentum, influencing both the mean velocity profile, as well as the turbulent diffusivity. For flexible canopies, the passage of the KH vortices generates a progressive wave along the canopy interface, termed monami. The KH vortices formed at the top of the canopy penetrate a distance δ e into the canopy. This penetration scale segregates the canopy into an upper layer of rapid transport and a lower layer of slow transport. Flushing of the upper canopy is enhanced by the energetic shear-scale vortices. In the lower layer turbulence is limited to length-scales set by the stem geometry, and the resulting transport is significantly slower than that of the upper layer.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdelrhman, M. (2003), Effect of eelgrass Zostera marina canopies on flow and transport, Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 248, 67–83.
Ackerman, J.D., and A. Okubo (1993), Reduced mixing in a marine macrophyte canopy, Functional Ecol. 7, 305–309.
Beavers, G., and D. Joseph (1967), Boundary conditions at a naturally permeable wall, J. Fluid Mechanics 30, 197–207.
Brown, G., and A. Roshko (1974), On density effects and large structure in turbulent mixing layers, J. Fluid Mechanics 64, 775–816.
Businger, J. (1975), Aerodynmiacs of vegetated surfaces. In: D.A. Devries and N.H. Afgan (eds.), Heat and Mass Transfer in the Biosphere. Part I. Transfer Processes in the Plant Environment, Scripta, Washington, DC.
Carollo, F., V. Ferro, and D. Termini (2002), Flow velocity measurements in vegetated channels, J. Hydraul. Eng. ASCE 128, 7, DOI: 10.1061/0733-9429.
Chambers, P., and E. Prepas (1994), Nutrient dynamics in riverbeds: the impact of sewage effluent and aquatic macrophytes, Water Research 28, 453–464.
Chandler, M., P. Colarusso, and R. Buchsbaum (1996), A study of eelgrass beds in Boston Harbor and northern Massachusetts bays, Office of Res. and Devel., US EPA, Narragansett, RI.
Chikwendu, S., and G. Ojiakor (1985), Slow-zone model for longitudinal dispersion in two-dimensional shear flows, J. Fluid Mechanics 152, 15–38.
Ciraolo, G., G. Ferreri, and G. LaLoggia (2006), Flow resistance of Posidonia Oceanica in shallow water. J. Hydraul. Res. 44, 2, 189–202.
Day, T. (1975), Longitudinal dispersion in natural channels, Water Resour. Res. 11, 6, 909–918.
Dimotakis, P., F. Debussy, and M. Koochesfahani (1981), Particle streak velocity field measurements in a two-dimensional mixing layer, Phys. Fluids 24, 6, 95–999.
Dunn, C., F. Lopez, and M. Garcia (1996), Mean flow and turbulence in a laboratory channel with simulated vegetation, Hydraulic Eng. Ser. 51, University of Illinois, Urbana, IL.
Dwyer, M., E. Patton, and R. Shaw (1997), Turbulent kinetic energy budgets from a large-eddy simulation of airflow above and within a forest canopy, Bound.-Layer Meteor. 84, 23–43.
Finnigan, J. (1979), Turbulence in waving wheat: I. Mean statistics and honami, Bound.-Layer Meteor. 16, 181–211.
Finnigan, J. (2000), Turbulence in plant canopies, Ann. Rev. Fluid Mech. 32, 519–571.
Fitzmaurice, L., R. Shaw, K.U. Paw, and E. Patton (2004), Three-dimensional scalar microfront systems in a large-eddy simulation of vegetation canopy flow, Bound.-Layer Meteor. 112, 107–127.
Folkard, A. (2005), Hydrodynamics of model Posidonia oceanica patches in shallow water, Limnol. Oceanogr. 50, 5, 1592–1600.
Fonseca, M.S., and W.J. Kenworthy (1987), Effects of current on photosynthesis and distribution of seagrasses, Aquat. Bot. 27, 59–78.
Furukawa, K., E. Wolanski, and H. Mueller (1997), Currents and sediment transport in mangrove forests, Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 44, 301–310.
Ghisalberti, M. (2000), Mixing layers and coherent structures in vegetated aquatic flows, Massachusetts Instititute of Technology, Cambridge, MA, MS Thesis.
Ghisalberti, M. (2005), Momentum and scalar transport in vegetated shear flows, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, MA, PhD Thesis.
Ghisalberti, M. (2006), Vortex dynamics in obstructed flows. In: G.N. Ivey (ed.) Proc. Sixth I.S.S.F, University of Western Australia, Perth, Australia, 342–347.
Ghisalberti, M., and H. Nepf (2002), Mixing layers and coherent structures in vegetated aquatic flow, J. Geophys. Res. 107, C2, DOI: 10.1029/2001JC000871.
Ghisalberti, M., and H. Nepf (2005), Mass transfer in vegetated shear flows, Environ. Fluid Mech. 5, 6, 527–551, DOI: 10.1007/s10652-005-0419-1.
Ghisalberti, M., and H. Nepf (2006), The structure of the shear layer over rigid and flexible canopies, Environ. Fluid Mech. 6, 3, 277–301, DOI: 10.1007/s10652-006-0002-4
Grimond, C., and T. Oke (1999), Aerodynamic properties of urban areas derived from analysis of surface form, J. Appl. Meteorol. 38, 1262–1292.
Grizzle, R., F. Short, C. Newell, H. Hoven, and L. Kindblom (1996), Hydrodynamically induced synchronous waving of seagrasses: “monami” and its possible effects on larval mussel settlement, J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 206, 165–177.
Harvey, J., J. Saiers, and J. Newlin (2005), Solute transport and storage mechanisms in wetlands of the Everglades, South Florida. Water Resour. Res 41, W05009, DOI: 10.1029/2004WR003507.
Ho, C-M., Y. Zohar, J. Foss, and J. Buell (1991), Phase decorrelation of coherent structures in a free shear layer, J. Fluid Mechanics 230, 319–337.
Ikeda, S., and M. Kanazawa (1996), Three-dimensional organized vortices above flexible water plants, J. Hydraul. Eng. 122, 11, 634–640.
Kaimal, J., and J. Finnigan (1994), Atmospheric Boundary Layer Flows: Their Structure and Measurement, Oxford University Press, Oxford.
Katul, G., P. Wiberg, J. Albertson, and G. Hornberger (2002), A mixing layer theory for flow resistance in shallow streams, Water Resour. Res. 38, 11, 1250, DOI: 10.1029/2001WR000817.
Kemp, J., D. Harper, and G. Crosa (2000), The habitat-scale ecohydraulics of rivers, Ecol. Eng. 16, 17–29
Knutson, P., R. Brochu, W. Seelig, and M. Inskeep (1982), Wave damping in Spartina alterniflora marshes, Wetlands 2, 87–104.
Kouwen, N. (1992), Modern approach to design of grassed channels, J. Irrigation and Drainage Engng. 118, 5, 733–743.
Kouwen, N., and T. Unny (1973), Flexible roughness in open channels, J. Hydraul. Div. 99, HY5, 713–728.
Leonard, L., and M. Luther (1995), Flow hydrodynamics in tidal marsh canopies, Limnol. Oceanogr. 40, 1474–1484.
Leonard, L., and D. Reed (2002), Hydrodynamics and sediment transport through tidal marsh canopies, J. Coastal Res. 36, 459–469.
Lightbody, A., and H. Nepf (2006a), Prediction of velocity profiles and longitudinal dispersion in emergent salt marsh vegetation, Limnol. Oceanogr. 51, 1, 218–228.
Lightbody, A., and H. Nepf (2006b), Prediction of near-field shear dispersion in an emergent canopy with heterogeneous morphology, Env. Fluid Mech. 6, 5, DOI: 10.1007/s10652-006-9002-7.
Lopez, F., and M. Garcia (1998), Open-channel flow through simulated vegetation: suspended sediment transport modeling, Water Resour. Res. 34, 9, 2341–2352.
Mars, M., M. Kuruvilla and H. Goen (1999), The role of submergent macrophyte triglochin huegelii in domestic greywater treatment, Ecol. Eng. 12, 57–66.
Mazda, Y., E. Wolanski, B. King, A. Sase, D. Ohtsuka, and M. Magi (1997), Drag forces due to vegetation in mangrove swamps, Mangr. Salt Marsh. 1, 193–199.
Murphy, E., H. Nepf, and M. Ghisalberti (2007), Longitudinal dispersion in vegetated channels, Water Resour. Res. 43, W05438, DOI: 10.1029/2006WR005229.
Nepf, H. (1999), Drag, turbulence, and diffusion in flow through emergent vegetation, Water Resour. Res. 35, 479–489.
Nepf, H., and E. Vivoni (2000), Flow structure in depth-limited, vegetated flow, J. Geophys. Res. 105, 28, 547–557.
Nepf, H., M. Ghisalberti, B. White, and E. Murphy (2007), Retention time and dispersion associated with submerged aquatic canopies, Water Resour. Res. 43, W04422, DOI: 10.1029/2006WR005362.
Nikora, N., and V. Nikora (2007), A viscous drag concept for flow resistance in vegetated channels, Proc. of the 32 nd IAHR Congress, Venice, 1–6 July.
Nikora, V., K. Koll, S. McLean, A. Dittrich, and J. Aberle (2002), Zero-plane displacement for rough-bed open-channel flows. Proc. Intern. Conf. on Fluvial Hydraulics, River Flow, Louvain-la-Neuve, Belgium, September 4–6, 2002, 83–92.
Nikora, V., K. Koll, I. McEwan, S. McLean, and A. Dittrich (2004), Velocity distribution in the roughness layer of rough-bed flows, J. Hydraul. Eng. 130, 1036–1042, DOI: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9429(2004)130:10(1036).
Nikora, V., I. McEwan, S. McLean, S. Coleman, D. Pokrajac, and R. Walters (2007), Double-averaging concept for rough-bed open-channel and over-land flows: theoretical background, J. Hydraul. Eng. ASCE 133, 8, 873–883.
Panides, E., and R. Chevray (1990), Vortex dynamics in a plane, moderate-Reynolds-number shear layer, J. Fluid Mechanics 214, 411–435.
Plate, E., and A. Quraishi (1965), Modeling of velocity distributions inside and above tall crops, J. Appl. Meteorol. 4, 400–408.
Poggi, D., A. Porporato, L. Ridolfi, J. Albertson, and G. Katul (2004a), The effect of vegetation density on canopy sub-layer turbulence, Bound.-Layer Meteor. 111, 565–587.
Poggi, D., G. Katul, and J. Albertson (2004b), A note on the contribution of dispersive fluxes to momentum transfer within canopies, Bound.-Layer Meteor. 111, 615–621.
Poggi, D., G. Katul, and J. Albertson (2004c), Momentum transfer and turbulent kinetic energy budgets within a dense model canopy, Bound.-Layer Meteor. 111, 589–614.
Raupach, M. (1992), Drag and drag partition on rough surfaces, Bound.-Layer. Meteor. 60, 375–395.
Raupach, M. (1994), Simplified expressions for vegetation roughness length and zero-plane displacement as functions of canopy height and area index, Bound.-Layer Meteor. 71, 211–216.
Raupach, M., and R. Shaw (1982), Averaging procedures for flow within vegetation canopies, Bound.-Layer Meteor. 22, 79–90.
Raupach, M., and A. Thom (1981), Turbulence in and above plant canopies, Ann. Rev. Fluid Mech. 13, 97–129.
Raupach, M., J. Finnigan, and Y. Brunet (1996), Coherent eddies and turbulence in vegetation canopies: The mixing-layer analogy, Bound.-Layer Meteor. 60, 375–395.
Sand-Jensen, K. (1998), Influence of submerged macrophytes on sediment composition and near-bed flow in lowland streams, Freshwater. Biol. 39, 663–679, DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2427.1998.00316.x.
Schultz, M., H.-P. Kozerski, T. Pluntke, and K. Rinke (2002), The influence of macrophytes on sedimentation and nutrient retention in the lower River Spree, Water Resour. Res. 37, 569–578.
Shaw, R., and I. Seginer (1985), The dissipation of turbulence in plant canopies, 7th Symp. of the Amer. Meteor. Society on Turbulence and Diffusion, Boulder, CO, 200–203.
Shields, F.D., and J.R. Rigby (2005), River habitat quality from river velocities measured using acoustic doppler current profiler, Environmental Management, 36, 4, 565–575, DOI: 10.1007/s00267-004-0292-6.
Smith, R. (1981), A delay-diffusion description for contaminant dispersion, J. Fluid Mechanics 105, 469–486.
Tanino, Y., and H. Nepf (2008a), Laboratory investigation on mean drag in a random array of rigid, emergent cylinders, J. Hydraul. Eng. 134, 1, 34–41, DOI: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9429(2008)134:1(34).
Tanino, Y., and H. Nepf (2008b), Lateral dispersion in random cylinder arrays at high Reynolds number, J. Fluid Mechanics 600, 339–371.
Tennekes, H., and J. Lumley (1972), A First Course in Turbulence, MIT Press, Cambridge.
Thom, A. (1971), Momentum absorption by vegetation, Q. J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc. 97, 414–428.
Triska, F., R. Kennedy, G. Zellweger, and K. Bencala (1989), Retention and transport of nutrients in a third-order stream, Ecology 7, 1877–1892.
Tsujimoto, T. (2000), Fluvial processes in streams with vegetation, J. Hydraul. Res. 37, 789–804.
Valentine, E., and I. Wood (1977), Longitudinal dispersion with dead zones, J. Hydraul. Div. ASCE 103, 975–990.
Valiela, I., J. Teal, and W. Deuser (1978), The nature of growth forms in the salt marsh grass Spartina alterniflora, American Naturalist 112, 461–470.
Vereecken, H., J. Baetens, P. Viaene, F. Mostaert, and P. Meire (2006), Ecological management of aquatic plants: effects in lowland streams, Hydrobiologia 570, 1, 205–210.
Vivoni, E. (1998), Turbulence structure of a model eeagrass meadow, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, MS Thesis.
Wallace, S., D. Luketina, and R. Cox (1998), Large scale turbulence in seagrass canopies, Paper presented at 13th Australasian Fluid Mechanics Conference, Monash Univ., Melbourne, Victoria, Australia.
White, B., and H. Nepf (2003), Scalar transport in random cylinder arrays at moderate Reynolds number, J. Fluid Mechanics 487, 43–79.
White, B., and H. Nepf (2008), A vortex-based model of velocity and shear stress in a partially vegetated shallow channel, Water Resour. Res. 44, W01412, DOI: 10.1029/2006WR005651.
Wilcock, R., P. Champion, J. Nagels, and G. Crocker (1999), The influence of aquatic macrophytes on the hydraulic and physicochemical properties of a New Zealand lowland stream, Hydrobiologia 416, 1, 203–214.
Wilson, J.D. (1988), A second-order closure model for flow through vegetation, Bound.-Layer Meteor. 42, 371–392.
Wilson, C., T. Stoesser, P. Bates, and A. Bateman Pinzen (2003), Open channel flow through different forms of submerged flexible vegetation. J. Hydraul. Eng. 129, 847–853, DOI: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9429(2003)129:11(847).
Winant, C., and F. Browand (1974), Vortex pairing, the mechanism of turbulent mixing-layer growth, at moderate Reynolds number, J. Fluid Mechanics 63, 237–255.
Wu, F.-C., H.-W. Shen, and Y.-J. Chou (1999), Variation of roughness coefficients for unsubmerged and submerged vegetation, J. Hydraul. Eng. 125, 9, 934–942.
Wygnanski, I., and H. Fiedler (1970), The two-dimensional mixing region. J. Fluid Mechanics 41, 327–361.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nepf, H., Ghisalberti, M. Flow and transport in channels with submerged vegetation. Acta Geophys. 56, 753–777 (2008). https://doi.org/10.2478/s11600-008-0017-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2478/s11600-008-0017-y