| Citation: |
|
All-optical logic devices based on black arsenic–phosphorus with strong nonlinear optical response and high stability
-
Abstract
The Kerr nonlinearity in two-dimensional (2D) nanomaterials is emerging as an appealing and intriguing research area due to their prominent light processing, modulation, and manipulation abilities. In this contribution, 2D black arsenic-phosphorus (B-AsP) nanosheets (NSs) were applied in nonlinear photonic devices based on spatial self-phase modulation (SSPM) method. By applying the Kerr nonlinearity in 2D B-AsP, an all-optical phase-modulated system is proposed to realize the functions of “on” and “off” in all-optical switching. By using the same all-optical phase-modulated system, another optical logic gate is proposed, and the logical “or” function is obtained based on the 2D B-AsP NSs dispersions. Moreover, by using the SSPM method, a 2D B-AsP/SnS2 hybrid structure is fabricated, and the result illustrates that the hybrid structure possesses the ability of the unidirectional nonlinear excitation, which helps in obtaining the function of spatial asymmetric light propagation. This function is considered an important prerequisite for the realization of diode functionalization, which is believed to be a factor in important basis for the design of isolators as well. The initial investigations indicate that 2D B-AsP is applicable for designing optical logical devices, which can be considered as an important development in all-optical information processing. -

-
References
[1] Paredes-Barato D, Adams CS. All-optical quantum information processing using rydberg gates. Phys Rev Lett 112, 040501 (2014). doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.112.040501 [2] Larger L, Soriano MC, Brunner D, Appeltant L, Gutierrez JM et al. Photonic information processing beyond Turing: an optoelectronic implementation of reservoir computing. Opt Express 20, 3241–3249 (2012). doi: 10.1364/OE.20.003241 [3] Wang C, Chen QY, Chen HL, Liu J, Song YF et al. Boron quantum dots all-optical modulator based on efficient photothermal effect. Opto-Electron Adv 4, 200032 (2021). [4] Zheng JL, Tang X, Yang ZH, Liang ZM, Chen YX et al. Few-layer phosphorene-decorated microfiber for all-optical thresholding and optical modulation. Adv Opt Mater 5, 1700026 (2017). doi: 10.1002/adom.201700026 [5] Wu LM, Huang WC, Wang YZ, Zhao JL, Ma DT et al. 2D tellurium based high-performance all-optical nonlinear photonic devices. Adv Funct Mater 29, 1806346 (2019). doi: 10.1002/adfm.201806346 [6] Liao K, Chen Y, Yu ZC, Hu XY, Wang XY et al. All-optical computing based on convolutional neural networks. Opto-Electron Adv 4, 200060 (2021). [7] Lu L, Wang WH, Wu LM, Jiang XT, Xiang YJ et al. All-optical switching of two continuous waves in few layer bismuthene based on spatial cross-phase modulation. ACS Photonics 4, 2852–2861 (2017). doi: 10.1021/acsphotonics.7b00849 [8] Wu YL, Wu Q, Sun F, Cheng C, Meng S et al. Emergence of electron coherence and two-color all-optical switching in MoS2 based on spatial self-phase modulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 112, 11800–11805 (2015). doi: 10.1073/pnas.1504920112 [9] Ji W, Chen WZ, Lim S, Lin JY, Guo ZX. Gravitation-dependent, thermally-induced self-diffraction in carbon nanotube solutions. Opt Express 14, 8958–8966 (2006). doi: 10.1364/OE.14.008958 [10] Wu R, Zhang YL, Yan SC, Bian F, Wang WL et al. Purely coherent nonlinear optical response in solution dispersions of graphene sheets. Nano Lett 11, 5159–5164 (2011). doi: 10.1021/nl2023405 [11] Wang GZ, Zhang SF, Umran FA, Cheng X, Dong NN et al. Tunable effective nonlinear refractive index of graphene dispersions during the distortion of spatial self-phase modulation. Appl Phys Lett 104, 141909 (2014). doi: 10.1063/1.4871092 [12] Li LK, Yu YJ, Ye GJ, Ge QQ, Ou XD et al. Black phosphorus field-effect transistors. Nat Nanotechnol 9, 372–377 (2014). doi: 10.1038/nnano.2014.35 [13] Liu H, Neal AT, Zhu Z, Luo Z, Xu XF et al. Phosphorene: an unexplored 2D semiconductor with a high hole mobility. ACS Nano 8, 4033–4041 (2014). doi: 10.1021/nn501226z [14] Liu H, Du YC, Deng YX, Ye PD. Semiconducting black phosphorus: synthesis, transport properties and electronic applications. Chem Soc Rev 44, 2732–2743 (2015). doi: 10.1039/C4CS00257A [15] Hao CX, Wen FS, Xiang JY, Yuan SJ, Yang BC et al. Liquid-exfoliated black phosphorous nanosheet thin films for flexible resistive random access memory applications. Adv Funct Mater 26, 2016–2024 (2016). doi: 10.1002/adfm.201504187 [16] Han ST, Hu L, Wang XD, Zhou Y, Zeng YJ et al. Black phosphorus quantum dots with tunable memory properties and multilevel resistive switching characteristics. Adv Sci 4, 1600435 (2017). doi: 10.1002/advs.201600435 [17] Zheng JL, Yang ZH, Si C, Liang ZM, Chen X et al. Black phosphorus based all-optical-signal-processing: toward high performances and enhanced stability. ACS Photonics 4, 1466–1476 (2017). doi: 10.1021/acsphotonics.7b00231 [18] Wang K, Chen YX, Zheng JL, Ge YQ, Ji JH et al. Black phosphorus quantum dot based all-optical signal processing: ultrafast optical switching and wavelength converting. Nanotechnology 30, 415202 (2019). doi: 10.1088/1361-6528/ab31b4 [19] Qiu M, Wang D, Liang WY, Liu LP, Zhang Y et al. Novel concept of the smart NIR-light–controlled drug release of black phosphorus nanostructure for cancer therapy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 115, 501–506 (2018). doi: 10.1073/pnas.1714421115 [20] Tao W, Zhu XB, Yu XH, Zeng XW, Xiao QL et al. Black phosphorus nanosheets as a robust delivery platform for cancer theranostics. Adv Mater 29, 1603276 (2017). doi: 10.1002/adma.201603276 [21] Hu W, Lin L, Yang C, Dai J, Yang JL. Edge-modified phosphorene nanoflake heterojunctions as highly efficient solar cells. Nano Lett 16, 1675–1682 (2016). doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.5b04593 [22] Dai J, Zeng XC. Bilayer phosphorene: effect of stacking order on bandgap and its potential applications in thin-film solar cells. J Phys Chem Lett 5, 1289–1293 (2014). doi: 10.1021/jz500409m [23] Abbas AN, Liu BL, Chen L, Ma YQ, Cong S et al. Black phosphorus gas sensors. ACS Nano 9, 5618–5624 (2015). doi: 10.1021/acsnano.5b01961 [24] Wu LM, Guo J, Wang QK, Lu SB, Dai XY et al. Sensitivity enhancement by using few-layer black phosphorus-graphene/TMDCs heterostructure in surface plasmon resonance biochemical sensor. Sens Actuators B Chem 249, 542–548 (2017). doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2017.04.110 [25] Zhang JD, Yu XF, Han WJ, Lv BS, Li XH et al. Broadband spatial self-phase modulation of black phosphorous. Opt Lett 41, 1704–1707 (2016). doi: 10.1364/OL.41.001704 [26] Xu YH, Wang WX, Ge YQ, Guo HY, Zhang XJ et al. Stabilization of black phosphorous quantum dots in pmma nanofiber film and broadband nonlinear optics and ultrafast photonics application. Adv Funct Mater 27, 1702437 (2017). doi: 10.1002/adfm.201702437 [27] Doganov RA, O’Farrell ECT, Koenig SP, Yeo YT, Ziletti A et al. Transport properties of pristine few-layer black phosphorus by van der Waals passivation in an inert atmosphere. Nat Commun 6, 6647 (2015). doi: 10.1038/ncomms7647 [28] Favron A, Gaufrès E, Fossard F, Phaneuf-L’Heureux AL, Tang NYW et al. Photooxidation and quantum confinement effects in exfoliated black phosphorus. Nat Mater 14, 826–832 (2015). doi: 10.1038/nmat4299 [29] Wood JD, Wells SA, Jariwala D, Chen KS, Cho E et al. Effective passivation of exfoliated black phosphorus transistors against ambient degradation. Nano Lett 14, 6964–6970 (2014). doi: 10.1021/nl5032293 [30] Guo ZN, Chen S, Wang ZZ, Yang ZY, Liu F et al. Metal-ion-modified black phosphorus with enhanced stability and transistor performance. Adv Mater 29, 1703811 (2017). doi: 10.1002/adma.201703811 [31] Tang X, Liang WY, Zhao JL, Li ZJ, Qiu M et al. Fluorinated phosphorene: electrochemical synthesis, atomistic fluorination, and enhanced stability. Small 13, 1702739 (2017). doi: 10.1002/smll.201702739 [32] Zhao YT, Wang HY, Huang H, Xiao QL, Xu YH et al. Surface coordination of black phosphorus for robust air and water stability. Angew Chem Int Ed 55, 5003–5007 (2016). doi: 10.1002/anie.201512038 [33] Liu BL, Köpf M, Abbas AN, Wang XM, Guo QS et al. Black arsenic–phosphorus: layered anisotropic infrared semiconductors with highly tunable compositions and properties. Adv Mater 27, 4423–4429 (2015). doi: 10.1002/adma.201501758 [34] Long MS, Gao AY, Wang P, Xia H, Ott C et al. Room temperature high-detectivity mid-infrared photodetectors based on black arsenic phosphorus. Sci Adv 3, e1700589 (2017). doi: 10.1126/sciadv.1700589 [35] Yuan SF, Shen CF, Deng BC, Chen XL, Guo QS et al. Air-stable room-temperature mid-infrared photodetectors based on hBN/Black arsenic phosphorus/hBN heterostructures. Nano Lett 18, 3172–3179 (2018). doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.8b00835 [36] Amani M, Regan E, Bullock J, Ahn GH, Javey A. Mid-wave infrared photoconductors based on black phosphorus-arsenic alloys. ACS Nano 11, 11724–11731 (2017). doi: 10.1021/acsnano.7b07028 [37] Qiao JS, Kong XH, Hu ZX, Yang F, Ji W. High-mobility transport anisotropy and linear dichroism in few-layer black phosphorus. Nat Commun 5, 4475 (2014). doi: 10.1038/ncomms5475 [38] Keyes RW. The electrical properties of black phosphorus. Phys Rev 92, 580–584 (1953). doi: 10.1103/PhysRev.92.580 [39] Warschauer D. Electrical and optical properties of crystalline black phosphorus. J Appl Phys 34, 1853–1860 (1963). doi: 10.1063/1.1729699 [40] Kresse G, Furthmüller J. Efficient iterative schemes for ab initio total-energy calculations using a plane-wave basis set. Phys Rev B 54, 11169–11186 (1996). doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.54.11169 [41] Perdew JP, Burke K, Ernzerhof M. Generalized gradient approximation made simple. Phys Rev Lett 77, 3865–3868 (1996). doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.77.3865 [42] Kresse G, Joubert D. From ultrasoft pseudopotentials to the projector augmented-wave method. Phys Rev B 59, 1758–1775 (1999). [43] Durbin SD, Arakelian SM, Shen YR. Laser-induced diffraction rings from a nematic-liquid-crystal film. Opt Lett 6, 411–413 (1981). doi: 10.1364/OL.6.000411 [44] Wu LM, Dong YZ, Zhao JL, Ma DT, Huang WC et al. Kerr nonlinearity in 2D graphdiyne for passive photonic diodes. Adv Mater 31, 1807981 (2019). doi: 10.1002/adma.201807981 [45] Wu JJ, Tao YR, Wu XC, Chun Y. Nonlinear optical absorption of SnX2 (X=S, Se) semiconductor nanosheets. J Alloys Compd 713, 38–45 (2017). doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2017.04.177 [46] Ye GL, Gong YJ, Lei SD, He YM, Li B et al. Synthesis of large-scale atomic-layer SnS2 through chemical vapor deposition. Nano Res 10, 2386–2394 (2017). doi: 10.1007/s12274-017-1436-3 -
Supplementary Information
Supplementary information for All optical logic devices based on black arsenic–phosphorus with strong nonlinear optical response and high stability 
-
Access History

Article Metrics
-
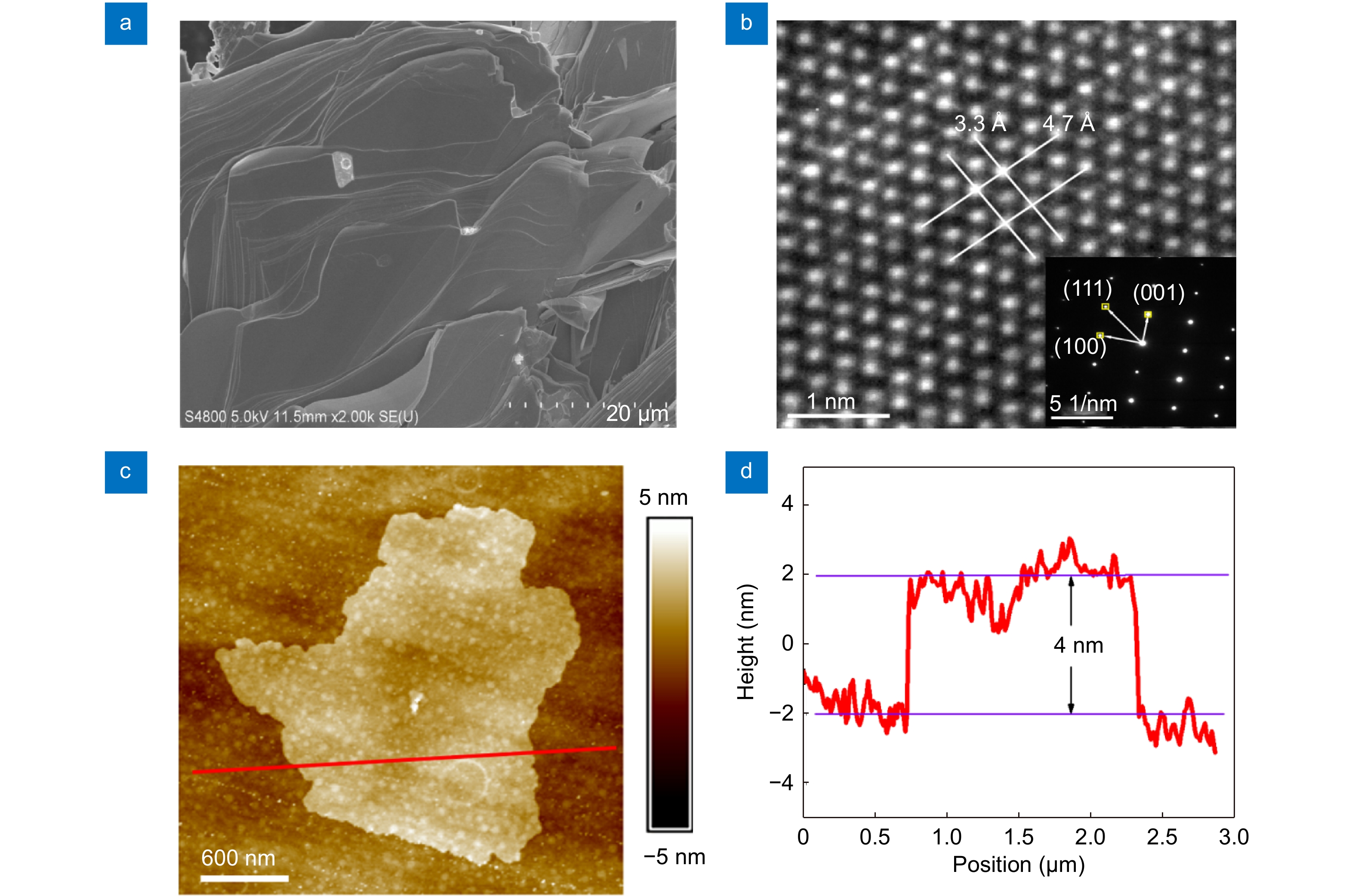
Figure 1.
(a) The SEM image of the layered B-AsP. (b) The high resolution TEM (HRTEM) image and the selected area electron diffraction (SAED) pattern of the 2D B-AsP. (c) The AFM image of 2D B-AsP. (d) The height profiles along the red line in (c).
-
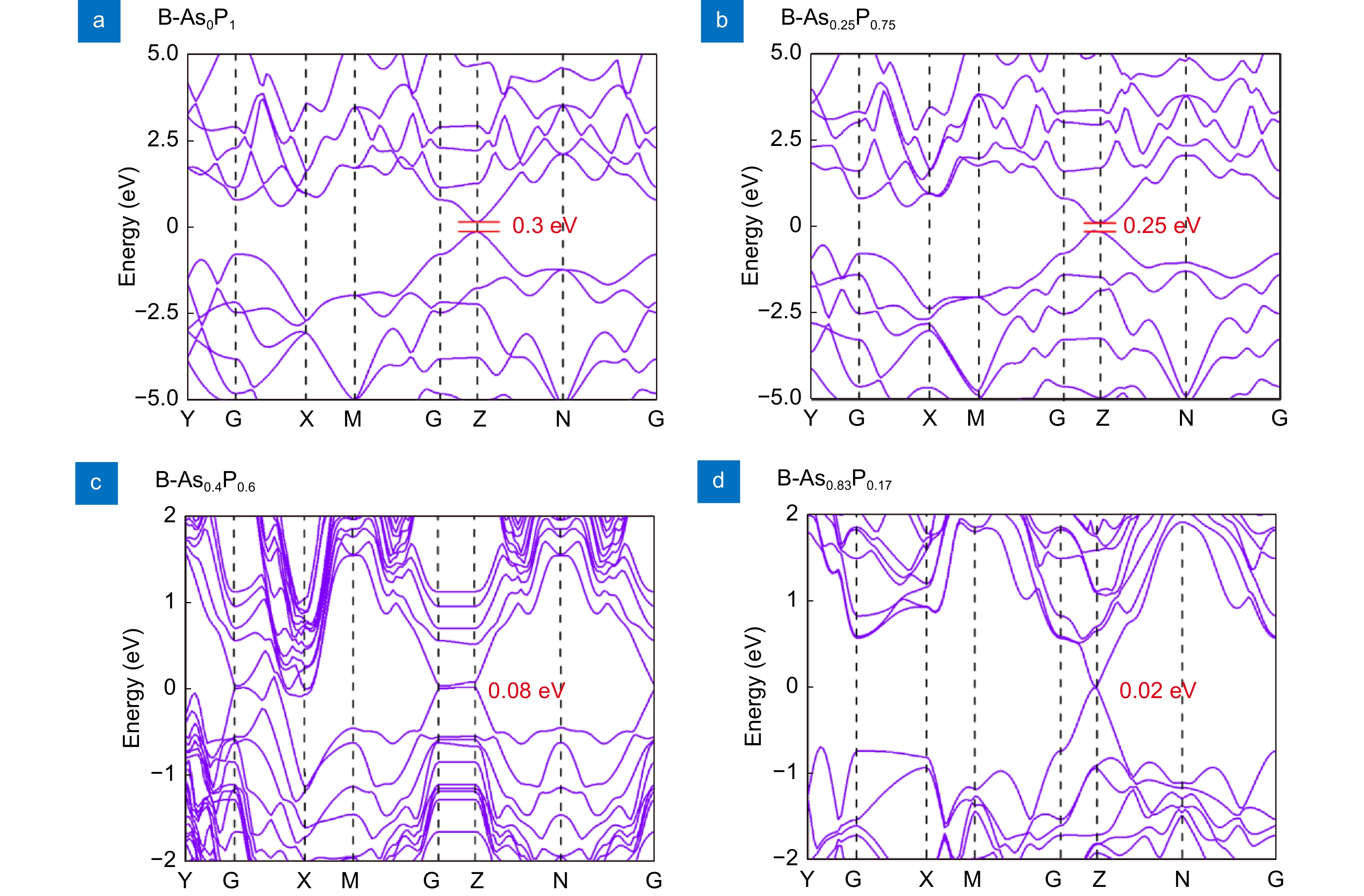
Figure 2.
Band gap structures of the B-AsxP1-x with different value of “x” (x = 0, 0.25, 0.4, and 0.83).
-
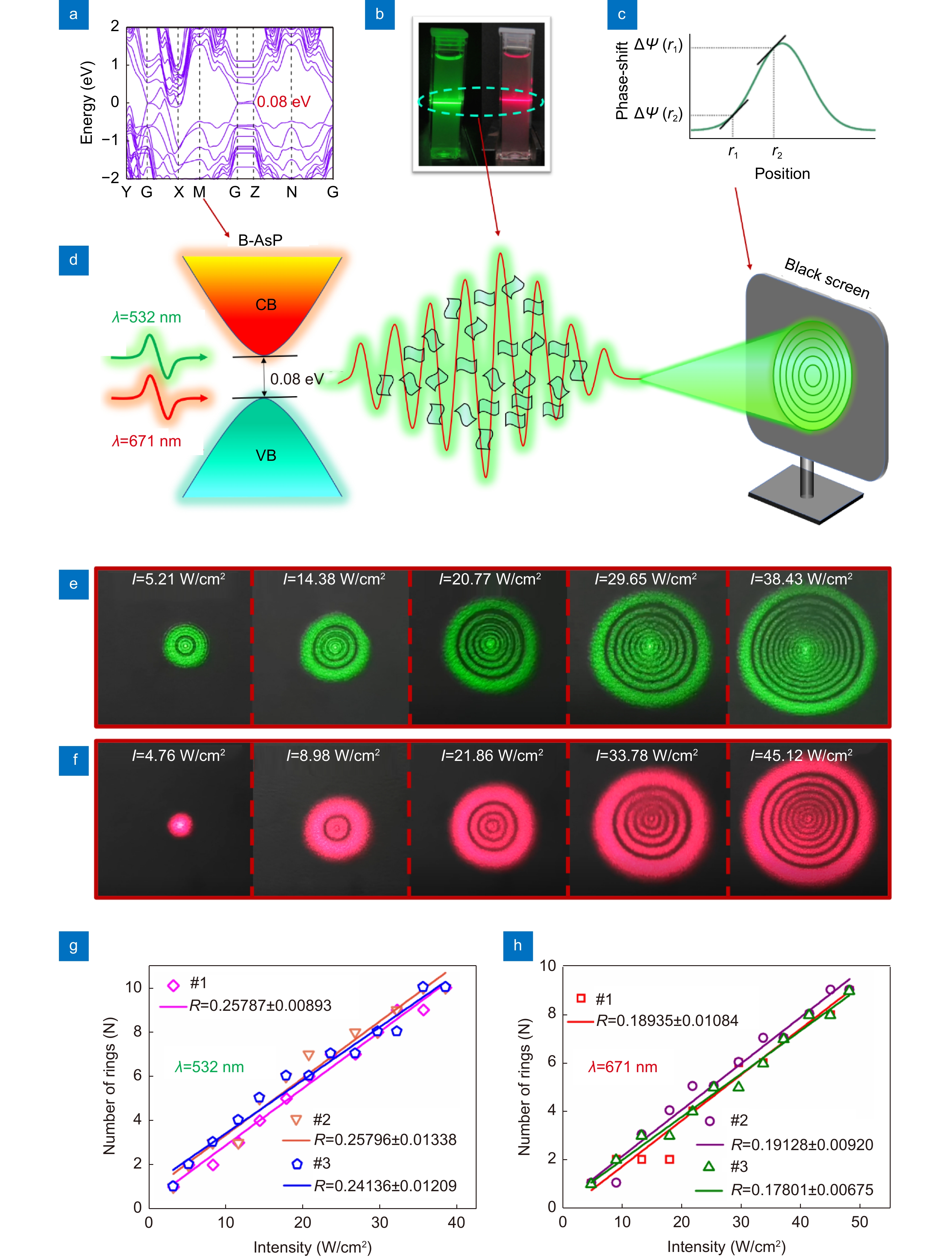
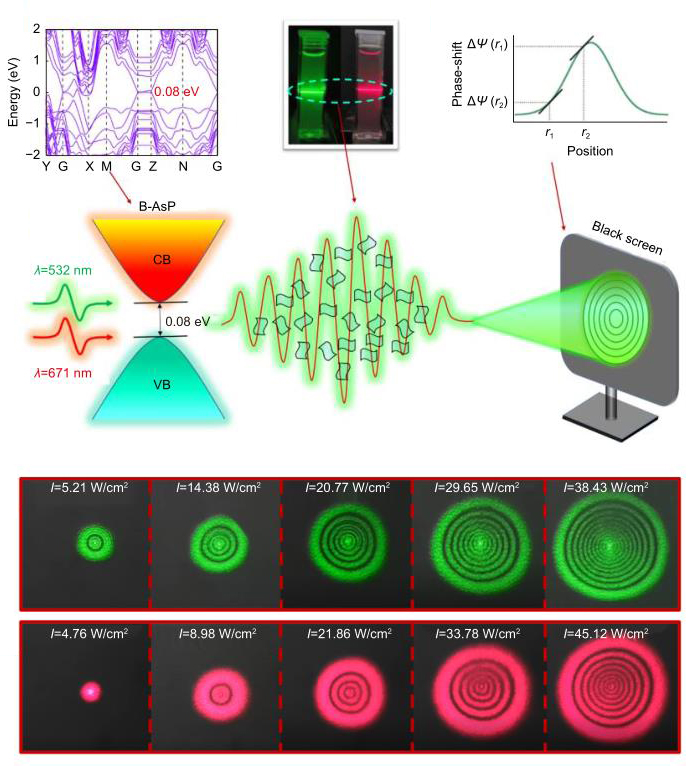
Figure 3.
(a) The band gap structure of the B-AsxP1-x (x = 0.4) NSs. (b) The 2D B-AsP NSs dispersions used in our experiment, and the Tyndall effect observed as the laser beams transmitted through the sample. (c) The phase-shift of the incident light caused by the Kerr nonlinearity in 2D B-AsP NSs. (d) Experimental schematic of the SSPM based on the 2D B-AsP NSs dispersions. (e, f) The intensity-dependent diffraction patterns generated from the 2D B-AsP NSs dispersions with the lasers of λ = 532 nm and 671 nm, respectively. (g, h) The nonlinear optical response (R) for the 2D B-AsP NSs dispersions with three repeated measurements at λ = 532 nm and 671 nm, respectively.
-
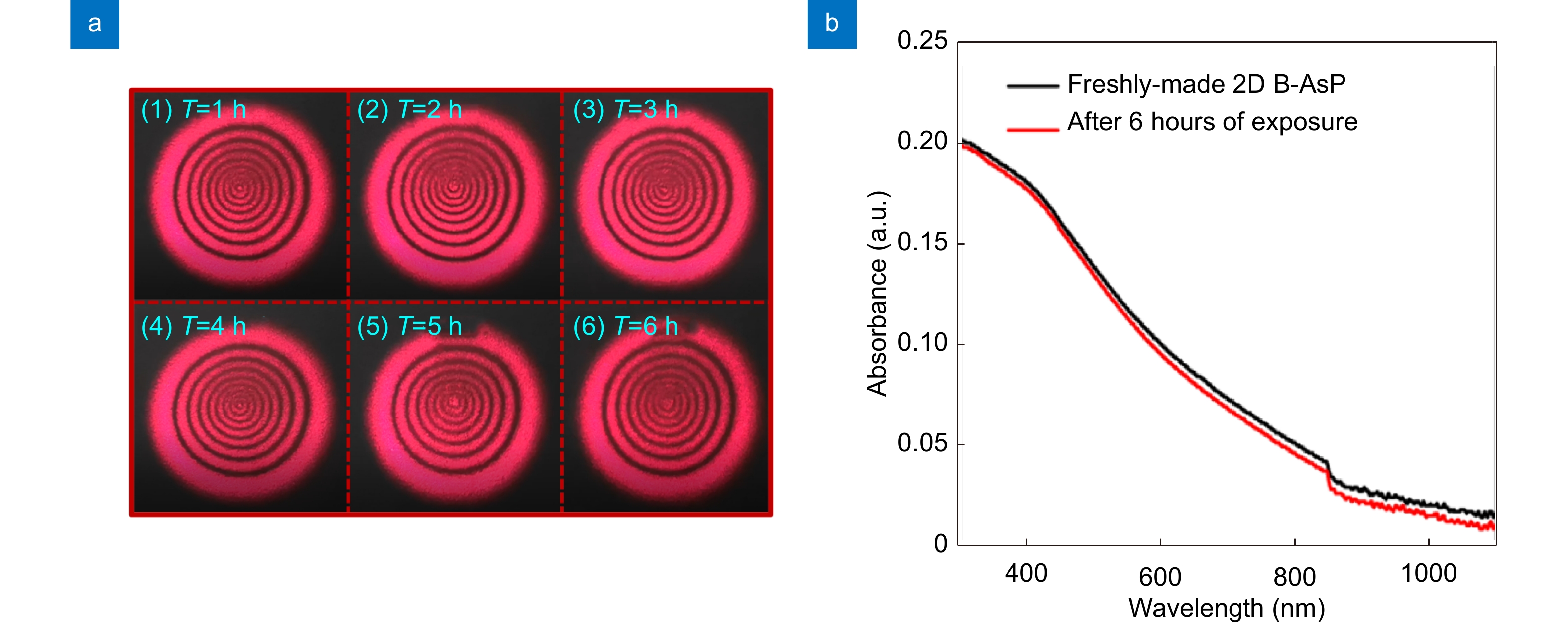
Figure 4.
(a) The diffraction patterns excited from the 2D B-AsP NSs dispersions with a high light intensity for consecutive 6 hours. (b) The absorption spectrums for the 2D B-AsP NSs dispersions before and after 6 hours of exposure.
-
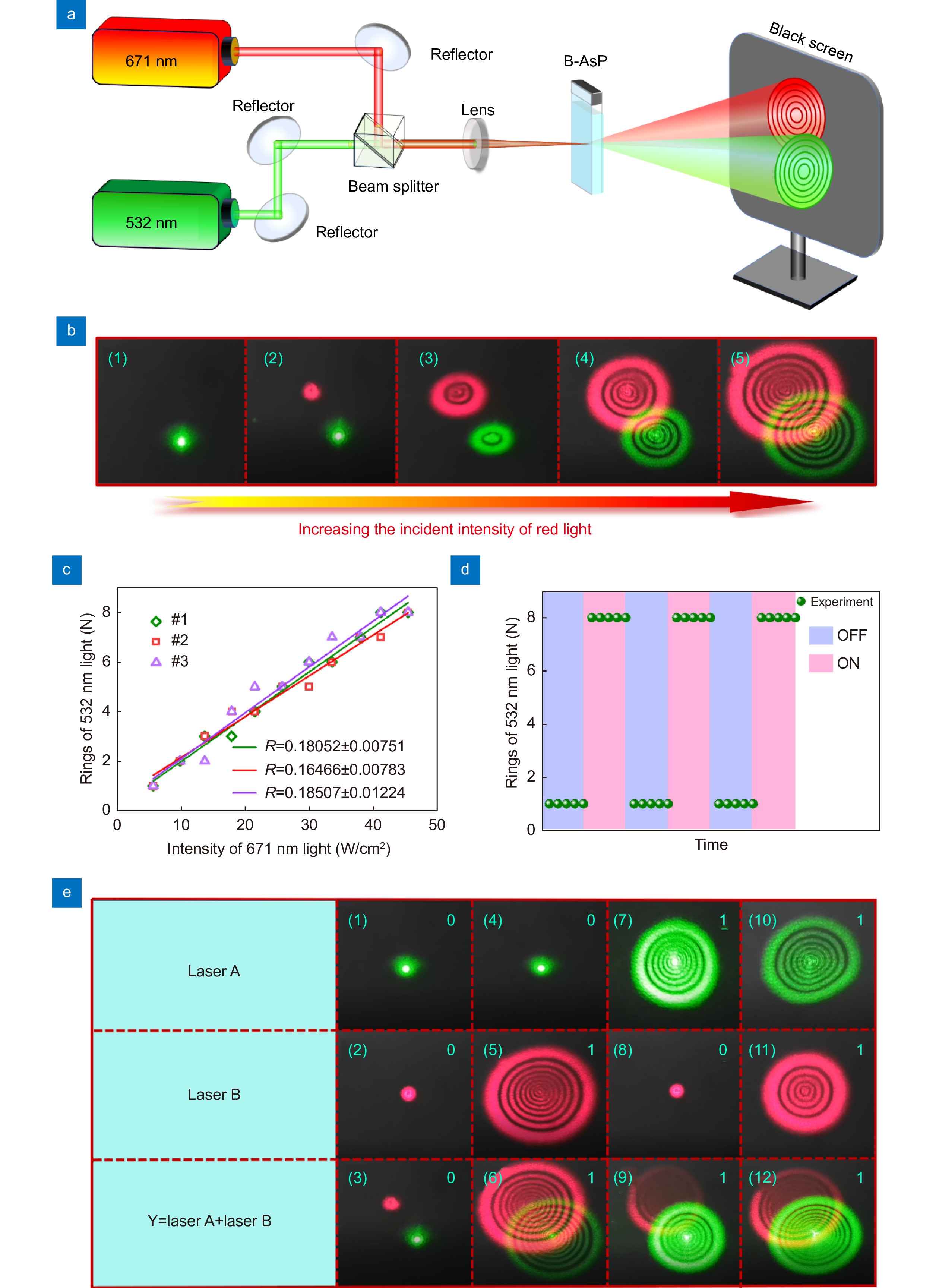
Figure 5.
(a) Experimental schematic of the 2D B-AsP-based all-optical phase modulated system. (b) The phase modulation of controlling light to signal light. (c) The number of diffraction rings modulated by the intensity of controlling light. (d) Result of the all-optical switching based on 2D B-AsP NSs to realize the functions of “on” and “off”. (e) 2D B-AsP NSs all-optical logical gate to achieve the “or” function.
-
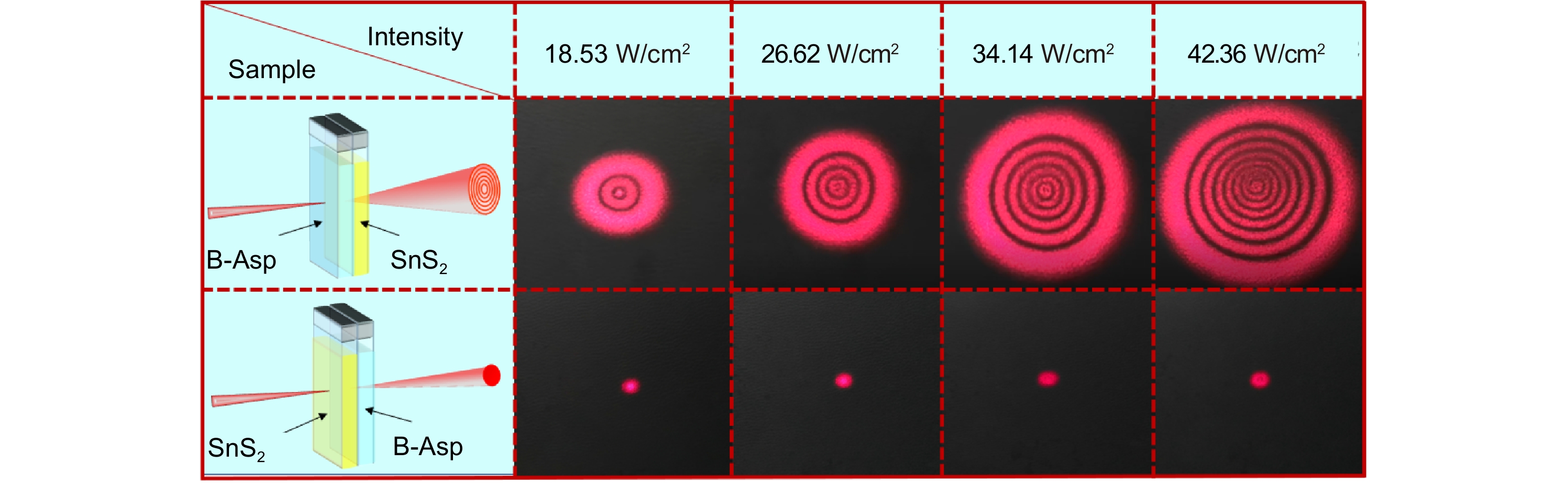
Figure 6.
The unidirectional nonlinear excitation in 2D B-AsP/ SnS2 hybrid structure to achieve the spatial asymmetric light propagation.
- Figure FIG. 1252..

 E-mail Alert
E-mail Alert RSS
RSS


 DownLoad:
DownLoad: