Abstract
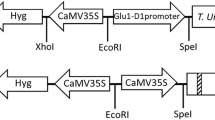
The biolistic transformation method was used for genetic improvement of three commercial cultivars of barley (Oksamytoviy, Vodogray, and Hetman). The plasmid pHLFTuBA containing target gene hLF encoding human lactoferrin under the control of the rice glutein B-1 promoter GluB-1 was used for transformation. The gene encoding mutant alfa-tubulin conferring resistance to trifluralin (dinitroaniline herbicide) was used as the selective marker. The screening of different trifluralin concentrations ranging from 0.1–30 μM was used for determination of selective concentration of the agent. Two transgenic barley lines of cultivars Oksamytoviy and Hetman’s callus line were selected after 2–3 months of cultivation on 10 μM of trifluralin. To confirm stable integration of the transformed gene, the PCR analysis of leafs from regenerated plant after their adaptation on the ground was carried out. The 734 bp fragment of the target gene was amplified from both regenerated plants.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tanasienko, I.V., Yemets, A.I., and Blume, Ya.B., Estimation of the Efficiency of Callus Formation and Regeneration in Barley Spring Varieties Zoned in Ukraine, Cytol. Genet., 2009, vol. 43, pp. 12–19.
Farago, J. and Nemcova, L., Regeneration of Biolaphos Resistant Plants after Biolistic Transformation of Two Commercial Cultivars of Spring Barley Hordeum vulgare L. Grown in Slovakia, Vedecke-Prace, 2001, vol. 30, pp. 169–176.
Manoharan, M. and Dahleen, L.S., Genetic Transformation of Commercial Barley Hordeum vulgare L. Cultivar Conlon by Particle Bombardment of Callus, Plant Cell Rep., 2002, vol. 21, pp. 76–80.
Assem, S.K., Hussein Ebtissam, H.A., Saad, M.E., El-Itriby, H.A., and Madkour, M.A., Comparison of the Efficiency of Some Novel Maize Promoters in Monocot and Dicot Plants, Arab J. Biotech., 2002, vol. 5, pp. 57–66.
Wang, M., Abbott, D., Upadhyaya, N., Jacobsen, J., and Waterhouse, P., Agrobacterium Tumefaciens-Mediated Transformation of an Elite Australian Barley Cultivar with Virus Resistance and Reporter Genes, Aust. J. Plant Physiol., 2001, vol. 28, pp. 149–156.
Sharma, V., Monostori, T., Gobel, C., Hansch, R., Bittner, F., Wasternack, C., Feussner, I., Mendel, R., Hause, B., and Schulze, J., Transgenic Barley Overexpressing a 13-Lipoxygenase to Modify Oxylipin Signature, Phytochemistry, 2006, vol. 67, pp. 264–276.
Delhaize, E., Ryan, P., Hebb, D., Yamamoto, Y., Sasaki, T., and Matsumoto, H., Engineering High-Level Aluminum Tolerance in Barley with the ALMT1 Gene, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 2004, vol. 101, pp. 15249–15254.
Dahleen, L.S. and Manoharan, M., Recent Advances in Barley Transformation, In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol. Plant, 2007, vol. 43, pp. 493–506.
Ritala, A., Wahlstrom, E., Holkeri, H., Malkelainrn, K., Baez, J., Makinen, K., and Nuutila, A., Production of Recombinant Industrial Protein using Barley Cell Cultures, Protein Expr. Purif., 2008, vol. 59, pp. 274–281.
Adlerova, L., Bartoskova, A., and Faldyna, M., Lactoferrin: A Review, Vet. Med., 2008, vol. 53, pp. 457–468.
Sorensen, M. and Sorensen, S., The Proteins in Whey, Comptes-rendus des Travaux du Laboratoire Carlsberg, 1939, vol. 23, pp. 55–99.
Yoo, Y., Watanabe, R., Koike, Y., Mitobe, M., Shimazaki, K., and Watanabe, S., Apoptosis in Human Leukemic Cells Induced by Lactofer-Ricin, a Bovine Milk Protein-Derived Peptide: Involvement of Reactive Oxygen Species, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 1997, vol. 237, pp. 624–628.
Eliassen, L.T., Berge, G., Sveinbjornsson, B., Svendsen, J.S., Vorland, L.H., and Rekdal, O., Evidence for a Direct Anti-Tumor Mechanism of Action of Bovine Lactoferricin, Anticancer Res., 2002, vol. 22, pp. 2703–2710.
Liang, Q. and Richardson, T., Expression and Characterization of Human Lactoferrin in Yeast Saccharomyces Cerevisiae, J. Arg. Food Chem., 1993, vol. 41, pp. 1800–1807.
Van Berkel, H., Nuijens, H., Van Veen, A., Abrahams, P., and Thomassen, J., The Protein Structure of Recombinant Human Lactoferrin Produced in the Milk of Transgenic Cows Closely Matches the Structure of Human Milk-Derived Lactoferrin, Transgenic Res., 2005, vol. 14, pp. 397–405.
Zhang, Z., Coyne, P., Vidaver, K., and Mitra, A., Expression of Human Lactoferrin cDNA Confers Resistance to Ralstonia solanacearum in Transgenic Tobacco Plants, Phytopathology, 1998, vol. 88, pp. 730–734.
Anzai, H., Takaiwa, F., and Katsumata, K., Production of Human Lactoferrin in Transgenic Plants, in Lactoferrin: Structure, Function and Applications, Shimazaki, K., Tsuda, H., Tomita, M., Kuwata, T., and Perraudin, P., Eds., 2000, pp. 265–271.
Ward, P., Piddington, C., Cunningham, G., Zhou, X., Wyatt, R., and Conneely, O., A System for Production of Commercial Quantities of Human Lactoferrin: A Broad Spectrum Natural Antibiotic, Biotechnology, 1995, vol. 13, pp. 498–503.
Nandi, N., Yalada, D., Lu, S., Nikolov, Z., Fujiyama, K., and Huang, N., Process Development and Economic Evolution of Recombinant Human Lactoferrin Expressed in Rice Grain, Transgenic Res., 2005, vol. 14, pp. 237–249.
Stefanova, G., Vlahova, M., and Atanassov, A., Production of Recombinant Human Lactoferrin from Transgenic Plants, Biol. Plant., 2008, vol. 52, pp. 423–428.
Chen, I., Thiruvengadam, V., Lin, W.-D., Chang, H.-H., and Hsu, W.-H., Lysine Racemase: A Novel Non-Antibiotic Selectable Marker for Plant Transformation, Plant. Mol. Biol., 2009, vol. 72, pp. 153–169.
Yemets, A., Radchuk, V., Bayer, O., Bayer, G., Pakhomov, A., Baird, V.W., and Blume, Ya.B., Development of Transformation Vectors Based upon a Modified Plant α-Tubulin Gene as the Selectable Marker, Cell Biol. Int., 2008, vol. 32, pp. 566–570.
Finer, J., Vain, P., Jones, M., and McMullen, M., Development of the Particle Inflow Gun for DNA Delivery to Plant Cells, Plant Cell Rep., 1992, vol. 11, pp. 232–238.
Abumhadi, N., Trifonova, A., Takumi, S., Nakamura, C., Todorovska, E., Getov, L., Christov, N., and Atanassov, A., Development of the Particle Inflow Gun and Optimizing the Particle Bombardment Method for Efficient Genetic Transformation in Mature Embryos of Cereals, Biotechnol. Biotec. Eq., 2001, vol. 15, pp. 87–96.
Lakin, G.F., Biometriya (Biometry), Moscow: Vysshaya shkola, 1990.
Hagio, T., Hirabayashi, T., Machii, H., and Tomotsune, H., Production of Fertile Transgenic Barley Hordeum vulgare L. Plant using the Hygromycin-Resistance Marker, Plant Cell Rep., 1995, vol. 14, pp. 329–334.
Ahlandsberg, S., Sathish, P., Sun, C., and Jansson, C., Green Fluorescent Protein as a Reporter System in the Transformation of Barley Cultivars, Physiol. Plant., 1999, vol. 107, pp. 194–200.
Cho, M.-J., Jiang, W., and Lemaux, G., Transformation of Recalcitrant Barley Cultivars through Improvement of Regenerability and Decreased Albinism, Plant Sci., 1998, vol. 138, pp. 229–244.
Tobias, D., Manoharan, M., Pritsch, C., and Dahleen, L., Cobombardment, Integration and Expression of Rice Chitinase and Thaumatin-Like Protein Genes in Barley (Hordeum vulgare cv. Conlon), Plant Cell Rep., 2007, vol. 26, pp. 631–639.
Wan, Y. and Lemaux, P.G., Generation of Large Numbers of Independently Transformed Fertile Barley Plant, Plant Physiol., 1994, vol. 104, pp. 37–48.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © I.V. Tanasienko, A.I. Yemets, Y.V. Pirko, V.I. Korhkovyy, N. Abumhadi, Ya.B. Blume, 2011, published in Tsitologiya i Genetika, 2011, Vol. 45, No. 1, pp. 3–10.
About this article
Cite this article
Tanasienko, I.V., Yemets, A.I., Pirko, Y.V. et al. Generation of transgenic barley lines producing human lactoferrin using mutant alpha-tubulin gene as the selective marker. Cytol. Genet. 45, 1–6 (2011). https://doi.org/10.3103/S0095452711010026
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3103/S0095452711010026