Abstract
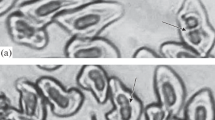
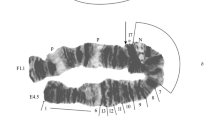
The study of variability of polytene chromosomes of Chironomids in water with different factors of pollution is given in the article. Special attention is drawn towards the reaction of Chironomid genome affected by radiation of Chernobyl region and heavy metals. Two types of reorganizations are discussed: inherited chromosomes, transmitted from year to year, from population to population, and somatic rare chromosomes covering small regions and influencing the duration of life of one generation. In polytene chromosomes, there are unique transcribing structures: nucleolar organizer (NOR) and Balbiani rings (BRs), which are significant for cell functioning. Functional alternations of these structures affected by radiation and chemical pollution are considered. The influence of mobile elements and repetitive DNA sequences on genome instability is explained. The genome alteration of a population can be considered adaptive, since it was necessary for species preservation during pollution.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Warwick, W.F., The effect of trophic contaminant interactions on chironomid community structure and succession (Diptera, Chironomidae), Neth. J. Aquat. Ecol., 1992, vol. 26, nos. 2/4, pp. 563–575.
Oliver, D.R., Life history of the Chironomidae, Ann. Rev. Entomol., 1971, vol. 16, pp. 211–230.
Toderash, I.K., Funktsional’noe znachenie khironomid v ekosistemakh vodoemov Moldavii (The Functional Significance of Chironomids in Ecosystems of Water Bodies of Moldova), Chisinau: Shtiintsa, 1984.
Balushkina, E.V., Funktsional’noe znachenie lichinok khironomid kontinental’nykh vodoemov (The Functional Significance of Chironomid Larvae in Continental Water Bodies), Leningrad: Nauka, 1987.
Warwick, W.F., Morphological deformities in Chironomidae (Diptera) larvae as biological indicators of toxic stress, in Toxic Contaminants and Ecosystem Health: A Great Lake Focus, Evans, M.S., Ed., Wiley Intersci., 1988, pp. 281–319.
Thienemann, A. and Strenzke, K., Larventyp und Imaginalart bei Chironomus s. s., Entomol. Tidskrift., 1951, vol. 72, pp. 1–21.
Makrushin, A.V., Biologicheskii analiz kachestva vody (Biological Analysis of Water Quality), Vinberg, G.G., Eds., Leningrad, 1974.
Saether, O.A., Chironomid communities as water quality indicators, Holarctic. Ecol., 1979, vol. 2, pp. 65–74.
Bakhtin, M.M. and Seisebaev, A.T., Some traits of indication of the status of the environment of the Semipalatinsk test site, Radioekol. Okhrana Okr. Sredy: Vestn. NYaTs RK, 2002, vol. 3, pp. 68–70.
Michailova, P. and Ilkova, Yu., Polytene chromosomes in the family Chironomidae, Diptera and their significance for biomonitoring, in Genome Biomarker Test System for Environmental Risk Assessment, Michailova, P. and Grozeva, S., Ed., Sofia–Moscow: Pensoft, 2013, pp. 60–98.
Kiknadze, I.I., Shilova, A.I., Kerkis, I.E., et al., Kariotipy i morfologiya lichinok triby Chironomini: atlas (Karyotypes and Morphology of the Larvae of the Tribe Chironomini: Atlas), Novosibirsk: Nauka, 1991.
Michailova, P., The polytene chromosomes and their significance to the systematics of the family Chironomidae, Diptera, Acta Zool. Fenn., 1989, vol. 186, pp. 1–107.
Keyl, H.G., Chromosomenevolution bei Chironomus. 2. Chromosomenumbauten und philognetische Beziehungen den Arten, Chromosoma, 1962, vol. 13, no. 4, pp. 464–514.
Michailova, P., Sella, G., and Petrova, N., Chironomids (Diptera) and their salivary gland chromosomes as indicators of trace metal genotoxicology, Ital. J. Zool., 2012, vol. 79, pp. 218–230.
Michailova, P. and Petrova, N., Chromosome polymorphism in geographically isolated populations of Chironomus plumosus L. (Chironomidae, Diptera), Cytobios, 1991, vol. 67, pp. 161–175.
Petrova, N., Chromosomal aberrations in three chironomid species (Diptera, Chironomidae) from the Chernobyl zone, Genetika, 1991, vol. 27, no. 5, pp. 836–848.
Petrova, N., Reorganizatsiya politennykh khromosom lichinok khironomid (Diptera, Chironomidae) i ikh reaktsiya na mutagennoe zagryaznenie okruzhayushchei sredy (Chernobyl’skaya katastrofa) (Reorganization of Polytene Chromosomes of the Larvae of Chironomids (Diptera, Chironomidae) and Their Response to Mutagenic Environmental Pollution (Chernobyl Disaster)), St. Petersburg, 2013.
Petrova, N., Vinokurova, N., Danilova, M., and Maslova, V., Seasonal variability of the karyotype structure of Chironomus plumosus (Diptera, Chironomidae) from a biotope of Kaliningrad, Tsitologiia, 2007, vol. 49, no. 10, pp. 901–904.
Michailova, P., Szarek-Gwiazda, E., and Kovnacki, A., Effect of contaminants on the genome of some species of genus Chironomus (Chironomidae, Diptera) live in sediments of Dunajec River and Czorsztyn Reservoir, Water Air Soil Pollut., 2009, vol. 202, pp. 245–258.
Michailova, P. and Mattinen, A., Cytotaxonomical variability of Chironomus plumosus L. and Chironomus anthracinus Zett. (Diptera, Chironomidae) from industrial and municipal polluted areas of Finland, Caryologia, 2000, vol. 53, pp. 69–81.
Michailova, P., Sella, G., and Petrova, N., Polytene chromosomes of Chironomidae (Diptera) as a bioassay of trace-metal-induced genome instability, in Proc. 18th Int. Symp. on Chironomidae, Fauna Norvegica, 2012, vol. 31, pp. 227–234.
Sella, G., Bovero, S., Ginepro, M., et al., Inherited and somatic cytogenetic variability in Palaearctic populations of Chironomus riparius Meigen (Diptera, Chironomidae), Genome, 2004, vol. 47, pp. 332–344.
Ilkova, J., Michailova, P., Thomas, A., and White, K., Genome instability of Chironomus riparius Mg. (Diptera, Chironomidae) from polluted water basins in Bulgaria, Ecol. Balkan, 2014, vol. 5, pp. 1–8.
Kiknadze, I.I., Istomina, A.G., Gunderina, L.I., et al., Cytogenetic monitoring of natural populations of chironomids of Altai under anthropogenic pollution, in Genetichesakie effekty antropogennykh faktorov sredy (Genetic Effects of Anthropogenic Environmental Factors), Novosibirsk, 1993, pp. 62–79.
Blaylock, B.G., Chromosomal polymorphism in irradiated natural populations of Chironomus, Genetics, 1966, vol. 53, pp. 131–136.
Blaylock, B.G., The production of chromosome aberration in Chironomus riparius (Diptera, Chironomidae) by tritiated water, Canad. Entomol., 1971, vol. 103, pp. 448–453.
Barsiene, J., Barsyte, D., and Taletiene, A., Viviparid mollusks as bioindicators of clastogenic and aneugenic effects in aquatic systems, Biologia, 1997, vol. 4, pp. 5–7.
Bentivegna, C. and Cooper, R., Reduced chromosomal puffing in Chironomus tentans as a biomarker for potentially genotoxic substances, Environ. Toxicol. Chem., 1993, vol. 12, pp. 1001–1011.
Barsiene, J., Chromosome set changes in Molluscas from highly polluted habitats, in Genetics and Evolution of Aquatic Organisms, Beaumont, A., Ed., London, 1994, pp. 434–447.
Hudson, L. and Ciburowski, J., Teratogenic and genotoxic responses of larval Chironomus salinarius group (Diptera, Chironomidae) to contaminated sediment, Environ. Toxicol. Chem., 1996, vol. 15, pp. 1375–1381.
Bhattacharyay, G., Sadhu, A., Mazumdar, A., and Chaudhuri, P., Antennal deformities of chironomid larvae and their use in biomonitoring of heavy metal pollutions in the River Damodar of West Bengal, India, Environ. Monitor. Ass., 2005, vol. 108, pp. 66–84.
Gutknecht, J., Inorganic mercury (Hg2) transport through lipid bilayer membranes, J. Membr. Biol., 1981, vol. 61, pp. 61–66.
Simkiss, K., Lipid solubility of heavy metals in saline solutions, J. Mar. Biol., 1983, vol. 63, no. 1, pp. 1–7.
De Bisthoven, L.G.J., Timmermans, K.R., and Ollevier, F., The concentration of cadmium, lead, copper and zinc in Chironomus riparius larvae with deformed versus normal menta, Hydrobiologia, 1992, vol. 239, no. 1, pp. 141–149.
Todorova, J., Population cytotaxonomical variability of model chironomid species (Diptera), Extended Abstract of Thesis, Sofia, 2000.
Michailova, P., Petrova, N., Bovero, S., et al., Effect of environmental pollution on the chromosomal variability of Chironomus riparius Meigen (Diptera, Chironomidae) larvae from two piedmont stations, Genetics, 2000, vol. 108, pp. 171–180.
Vinogradova, E.B. and Petrova, N.A., The first finding of a synanthropic population of Chironomus riparius Meign 1804 (Diptera, Chironomidae) in the basements of apartment buildings in St. Petersburg and some of its biological characteristics, Entomol. Obozr., 2004, vol. 83, no. 2, pp. 26–29.
Szarek-Gwiazda, E., Michailova, P., Ilkova, J., et al., The effect of long-term contamination by heavy metals on community and genome alterations of Chironomidae (Diptera) in a stream with mine drainage water (southern Poland), Ocean. Hydrobiol. Stud., 2013, vol. 42, no. 4, pp. 460–469.
Michailova, P., Ilkova, J., Duran, M., et al., Structural and functional alterations in salivary gland chromosomes and enzyme activity of Chironomus riparius Mg. (Diptera, Chironomidae) from anthropogenically polluted stations in Bulgaria and Turkey, Caryologia, 2012, vol. 65, no. 2, pp. 157–169.
Forstner, U. and Salomons, W., Trace metal analysis on polluted sediments. 1. Assessment of sources and intensities, Environ. Technol. Lett., 1980, vol. 1, no. 11, pp. 494–505.
Sella, G., Robotti, C., Michailova, P., and Ramella, L., Repetitive DNA size variation in three sections of the chromosome EF in a population of Chironomus riparius Mg (Diptera, Chironomidae) from Piedmont (Italy), Caryologia, 2001, vol. 54, no. 2, pp. 155–160.
Wieslander, L., The balbiani ring multigene family: coding sequences and evolution of a tissue-specific function, Prog. Nucl. Acids Res. Mol. Biol., 1994, vol. 48, pp. 275–313.
Michailova, P., Ilkova, J., Cervella, P., et al., Nor activity in Chironomus riparius Mg. (Diptera, Chironomidae) is affected by chronic exposure to trace metal pollution, Compt. Rendus Acad. Bulg. Sci., 2013, vol. 66, no. 9, pp. 1273–1278.
Il’inskaya, N.B., A Method for Determination of IntraInstar Stages of Development and Gender in Chironomid Larvae, in Metodicheskoe posobie po izucheniyu khironomid (A Guide to the Study of Chironomids), Akhrorov, F., Ed., Dushanbe: Donish, 1982, pp. 30–43.
Kiknadze, I.I. Comparative characteristics of puffing in salivary gland chromosomes of Chironomus thummi in the larval development and metamorphosis. 1. Puffing in chromosome IV, Tsitologiia, 1976, no. 11, pp. 1322–1329.
Kiknadze, I.I., Comparative characteristics of puffing in salivary gland chromosomes of Chironomus thummi in the larval development and metamorphosis. 1. Puffing in chromosomes I, II, and III, Tsitologiia, 1978, vol.20.
Michailova, P., Ilkova, J., Kerr, R., and White, K., Chromosome variability in Chironomus acidophilus Keyl from the Afon Goach, UK,, a river subject to long-term metal pollution, Aquatic Insects, 2009, vol. 31, pp. 213–225.
McClintock, B., The significance of responses of the genome to challenge, Science, 1984, vol. 226, pp. 792–801.
Michailova, P., Ilkova, J., Hankeln, T., et al., Somatic breakpoints, distribution of repetitive DNA and non-LTR retrotransposones insertion sites in the chromosomes of Chironomus piger Strenzke (Diptera, Chironomidae), Genetics, 2009, vol. 135, pp. 137–148.
Ilkova, J., Cervella, P., Zampicinini, G.P., et al., Chromosomal breakpoints and transposable-element-insertion sites in salivary gland chromosomes of Chironomus riparius Meigen (Diptera, Chironomidae) from trace metal polluted stations, Acta Zool. Bulg., 2013, vol. 65, no. 1, pp. 63–79.
Golubovskii, M.D., Vek genetiki: evolyutsiya idei i ponyatii (The Century of Genetics: The Evolution of Ideas and Concepts), St. Petersburg, 2000.
Michailova, P., Petrova, N,, Ramella, L., et al., Cytogenetic characteristics of a population of Chironomus riparius (Diptera, Chironomidae) from a polluted Po river station, Genetics, 1996, vol. 98, pp. 161–178.
Michailova, P., Petrova, N., Sella, G., et al., Cenotoxic effects of chromium on polytene chromosomes of Chironomus riparius Meigen 1804 (diptera. Chironomidae), Caryologia, 2001, vol. 54, no. 1, pp. 59–71.
Michailova, P., Ilkova, J., and White, K., Functional and structural rearrangements of salivary gland chromosomes of Chironomus riparius Mg. (Diptera, Chironomidae) in response to freshly neutralized aluminium, Environ. Pol., 2003, vol. 123, pp. 193–207.
Fischer, J., Zur fortplanzungsbiologie von Chironomus nuditarsis, Rev. Zool., 1996, vol. 76, pp. 23–35.
Michailova, P., Method of breeding the species from family Chironomidae, Diptera in experimental conditions, Compt. Rendus Acad. Bulg. Sci., 1985, vol. 38, no. 9, pp. 1179–1181.
Garcia-Sagredo, J.M., Fifty years of cytogenetics: a parallel view of the evolution of cytogenetics and genotoxicology, Biochem. Biophys. Acta, 2008, vol. 1779, pp. 363–375.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © P. Michailova, N. Petrova, 2015, published in Tsitologiya i Genetika, 2015, Vol. 49, No. 4, pp. 61–70.
About this article
Cite this article
Michailova, P., Petrova, N. Bioindicator potential of cytogenetic variability in polytene chromosomes of chironomids (Diptera, Chironomidae) to assess environmental pollution. Cytol. Genet. 49, 262–269 (2015). https://doi.org/10.3103/S0095452715040064
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3103/S0095452715040064