Abstract
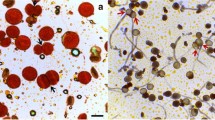
The intercellular translocation of chromatin material along with other cytoplasmic contents among the proximate meiocytes lying in close contact with each other commonly referred as cytomixis was reported during microsporogenesis in Phaseolus vulgaris L., a member of the family Fabaceae. The phenomenon of cytomixis was observed at three administered doses of gamma rays viz. 100, 200, and 300 Gy respectively in the diploid plants of Phaseolus vulgaris L. The gamma rays irradiated plants showed the characteristic feature of inter-meiocyte chromatin/chromosomes transmigration through various means such as channel formation, beak formation or by direct adhesion between the PMC’s (Pollen mother cells). The present study also reports the first instance of syncyte formation induced via cytomictic transmigration in Phaseolus vulgaris L. Though the frequency of syncyte formation was rather low yet these could play a significant role in plant evolution. It is speculated that syncyte enhances the ploidy level of plants by forming 2n gametes and may lead to the production of polyploid plants. The phenomenon of cytomixis shows a gradual inclination along with the increasing treatment doses of gamma rays. The preponderance of cytomixis was more frequent during meiosis I as compared to meiosis II. An interesting feature noticed during the present study was the channel formation among the microspores and fusion among the tetrads due to cell wall dissolution. The impact of this phenomenon is also visible on the development of post-meiotic products. The formation of heterosized pollen grains; a deviation from the normal pollen grains has also been reported. The production of gametes with unbalanced chromosomes is of utmost importance and should be given more attention in future studies as they possess the capability of inducing variations at the genomic level and can be further utilized in the improvement of germplasm.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arnoldy, W., Beitrage zur Morphologie der Gymnospermen. 4. Was sind die “Keimbläschen” oder “Hofmeisters-Körperchen” in der Eizelle der Abietineen?, Flora, 1900, vol. 87, pp. 194–204.
Koernicke, M., Uber ortsveranderung von Zellkarnern S.B. Niederhein, Ges Natur-U Heilkunde Bonn A, 1901.
Gates, R.R., Pollen formation in Oenothera gigas, Ann. Bot., 1911, vol. 25, no. 4, pp. 909–940.
Gottschalk, W., Chromosome and nucleus migration during microsporogenesis of Pisum satium, Nucleus, 1970, vol. 13, no. 1, pp. 1–9.
Bellucci, M., Roscini, C., and Mariani, A., Cytomixis in pollen mother cells of Medicago sativa L, J. Hered., 2003, vol. 94, no. 6, pp. 512–516.
Haroun, S.A., Al Shehri, A.M., and Al Wadie, H.M., Cytomixis in the microsporogenesis of Vicia faba L. (Fabaceae), Cytologia, 2004, vol. 69, no. 1, pp. 7–11.
Singhal, V.K. and Kumar, P., Impact of cytomixis on meiosis, pollen viability and pollen size in wild populations of Himalayan poppy (Meconopsis aculeate Royle), J. Biosci., 2008, vol. 33, no. 3, pp. 371–380.
Kumar, G. and Yadav, R.S., Induction of cytomixis affects microsporogenesis in Sesamum indicum L. (Pedaliaceae), Russ. J. Dev. Biol., 2012, vol. 43, pp. 209–214.
Rana, P.K., Kumar, P., and Singhal, V.K., Spindle irregularities, chromatin transfer, and chromatin stickiness during male meiosis in Anemone tetrasepala (Ranunculaceae), Turk. J. Bot., 2013, vol. 37, no. 1, pp. 167–176.
Sarvella, P., Cytomixis and loss of chromosomes in meiotic and somatic cells of Gossypium, Cytologia, 1958, vol. 23, pp. 14–24.
Tarkowska, J., Cytomixis in the epidermis of scales and leaves and in the meristems of root apex of Allium cepa L., Byul. Izobr., 1960, vol. 29, no. 1, pp. 149–168.
Koul, K.K., Cytomixis in pollen mother cells of Alopecurus arundinaceus Poir, Cytologia, 1990, vol. 55, no. 1, pp. 169–173.
Cooper, D.D., The transfer of deoxyribose nucleic acid from the tapetum to the microsporocytes at onset of meiosis, Am. Natur., 1952, vol. 86, pp. 219–229.
Klyuchareva, M.V., Extrusion of nuclear material in proembryos in graminaceous plants, Dokl. Akad. Nauk SSSR, 1983, vol. 269, no. 2, pp. 509–512.
Guzicka, M. and Wozny, A., Cytomixis in shoot apex of Norway spruce (Picea abies L. Karst.), Trees, 2004, vol. 18, no. 6, pp. 722–724.
Liu, H., Guo, G.-Q., He, Y.-K., Lu, Y.-P., and Zheng, G.-C., Visualization on intercellular movement of chromatin in intact living anthers of transgenic tobacco expressing histone 2B–CFP fusion protein, Caryologia, 2007, vol. 60, nos. 1/2, pp. 1–20.
Falistocco, E., Tosti, T., and Falcinelli, M., Cytomixis in pollen mother cells of diploid Dactylis, one of the origins of 2n gametes, J. Heredity, 1995, vol. 86, no. 6, pp. 448–453.
Lattoo, S.K., Khan, S., Bamotra, S., and Dhar, A.K., Cytomixis impairs meiosis and influences reproductive success in Chlorophytum comosum (Thunb.) Jacq.—an additional strategy and possible implications, J. Biosci., 2006, vol. 31, no. 5, pp. 629–637.
de Nettancourt, D. and Grant, W.F., La cytogenetiquede Lotus (Leguminosae). III. Un cas de Cytomixie dans un hybride interspecifique, Cytologia, 1964, vol. 29, no. 2, pp. 191–195.
Salesses, G., Sur le phenomene de cytomixie chez des hybrids triploids de prunier. Consequences genetiques possible, Ann. Amelior. Plant., 1970, vol. 20, pp. 383–388.
Mantu, D.E. and Sharma, A.K., Cytomixis in pollen mother cells of an apomictic ornamental Ervatamia diraricata Linn., Alston, Cytologia, 1983, vol. 48, no. 1, pp. 201–207.
Semyarkhina, S.Y.A. and Kuptsou, M.S., Cytomixis in various forms of sugar beet, Vests I ANBSSE Ser. Biyal., 1974, vol. 4, pp. 43–47.
Singhal, V.K., Gill, B.S., and Dhaliwal, R.S., Status of chromosomal diversity in the hardwood tree species of Punjab state, J. Cytol. Genet., 2007, vol. 8, pp. 67–83.
Kravchenko, L.N., Features of Meiosis in Wheat and Its Hybrids, Kishinev: Shtiintsa, 1977.
Kravets, E.A., Nature, significance and cytological consequences of cytomixis, Nytol. Genet., 2012, vol. 46, no. 3, pp. 188–195.
Zhang, W.C., Yan, W.M., and Lou, C.H., Mechanism of intercellular movement of protoplasm in wheat nucellus, Sci. China Chem., 1985, vol. 28, no. 11, pp. 1175–1187.
Ventela, S., Toppari, J., and Parvinen, M., Intercellular organelle traffic through cytoplasmic bridges in early spermatids of the rat: mechanisms of haploid gene product sharing, Mol. Biol. Cell, 2003, vol. 14, no. 7, pp. 2768–2780.
Kwiatkowska, M., Poplonska, K., and Wojtczak, A., Chara tomentosa antheridial plasmodesmata at various stages of spermatogenesis, Biol. Plant., 2003, vol. 46, no. 2, pp. 233–238.
McLean, B.G., Hempel, F.D., and Zambryski, P.C., Plant intercellular communication via plasmodesmata, Plant Cell, 1997, vol. 9, no. 7, pp. 1043–1054.
Milyaeva, E.D., On the problem of cytomixis during microsporogenesis, Byull. Gl. Bot Sada AN SSSR, 1965, vol. 59, pp. 53–57.
Mursalimov, S.R., Baiborodin, S.I., Sidorchuk, Yu.V., Shumny, V.K., and Deineko, E.V., Characteristics of the cytomictic channel formation in Nicotiana tabacum L. pollen mother cells, Cytol. Genet., 2010, vol. 44, no. 1, pp. 14–18.
Heslop-Harrison, J., Cytoplasmic connexions between angiosperm meiocytes, Ann. Bot., 1966, vol. 30, no. 2, pp. 221–222.
Wang, X.Y., Yu, C.H., Li, X., Wang, C.Y., and Zheng, G.C., Ultrastructural aspects and possible origin of cytoplasmic channels providing intercellular connection in vegetative tissues of anthers, Fiziol. Rast., 2004, vol. 51, no. 1, pp. 110–120.
Whelan, E.D.P., Discontinuities in the callose wall, intermeiocyte connections and cytomixis in angiosperm meiocytes, Can. J. Bot., 1974, vol. 52, no. 6, pp. 1219–1224.
Guo, G.-Q. and Zheng, G.-Ch., Hypothesis for the functions of intercellular bridges in male germ cell development and its cellular mechanisms, J. Theor. Biol., 2004, vol. 229, no. 1, pp. 139–146.
Amma, C.K.S., Namboodiri, A.N., Panikkar, A.O.N., and Sethuraj, M.R., Radiation induced male sterility in Hevea brasiliensis (Willd. ex Adr. de Juss.) Muell. Arg., Cytologia, 1990, vol. 55, no. 4, pp. 547–551.
Bedi, Y.S., Cytomixis in woody species, Proc. Indian Acad. Sci. (Plant Sci.), 1990, vol. 100, no. 4, pp. 233–238.
Dwivedi, N.K., Sikdar, A.K., Jolly, M.S., Susheelamma, B.N., and Suryanarayana, N., Induction of tetraploidy in colchicine-induced mutant of mulberry. 1. Morphological and cytological studies in cultivar Kanva-2, Indian J. Genet., 1988, vol. 48, no. 3, pp. 305–311.
Bhat, T.A., Sahba, P., and Khan, A.H., MMS-induced cytomixis in pollen mother cells of broad bean (Vicia faba L.), Turk. J. Bot., 2006, vol. 30, no. 4, pp. 273–279.
Takats, S.T., Chromatin extrusion and DNA transfer during microsporogenesis, Chromosoma, 1959, vol. 10, pp. 430–453.
Morisset, P., Cytomixis in the pollen mother cells of Ononis (Leguminosae), Can. J. Genet. Cytol., 1978, vol. 20, no. 3, pp. 383–388.
Mandal, G.D., Nandi, A.K., and Das, A.B., Cytomixis and associated meiotic abnormalities in pollen mother cells of Chlorophytum tuberosum (Roxb.) Baker, Cytologia, 2013, vol. 78, no. 2, pp. 157–162.
Levan, A., Syncyte formation in the pollen mother cells of haploid Phleum pretense, Hereditas, 1941, vol. 27, pp. 243–252.
Sarbhoy, R.K., Spontaneous occurrence of cytomixis and syndiploidy in Cyamopsis tetragonoloba (L.) Taub, Cytologia, 1980, vol. 45, no. 3, pp. 375–379.
Caetano-Pereira, C.M., Pagliarini, M.S., and Brasil, E.M., Cell fusion and chromatin degeneration in an inbred line of maize, Genet. Mol. Biol., 1999, vol. 22, no. 1, pp. 69–72.
Mendes-Bonato, A.B., Pagliarini, M.S., Silva, N., and Valle, C.B., Meiotic instability in invader plants of signal grass Brachiaria decumbens Stapf (Gramineae), Genet. Mol. Biol., 2001, vol. 23, no. 2, pp. 619–625.
Kim, J.S., Oginuma, K., and Tobe, H., Syncyte formation in the microsporangium of Chrysanthemum (Asteraceae): a pathway to infraspecific polyploidy, J. Plant Res., 2009, vol. 122, no. 4, pp. 439–444.
Wang, R.R.-C., Coenocytism, ameiosis, and chromosome diminution in intergeneric hybrids in the perennial Triticeae, Genome, 1988, vol. 30, no. 5, pp. 766–775.
Yen, C., Yan, J.L., and Sun, G.L., Intermeiocyte connections and cytomixis in intergeneric hybrid of Roegneria ciliaris (Trin.) Nevski with Psathyrostachys huashanica Keng, Cytologia, 1993, vol. 58, no. 2, pp. 187–193.
Ghaffari, S.M., Occurrence of diploid and polyploidy microspores in Sorghum bicolor (Poaceae) is the result of cytomixis, Afr. J. Biotechnol., 2006, vol. 5, no. 16, pp. 1450–1453.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The article is published in the original.
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, G., Chaudhary, N. Induced cytomictic variations and syncyte formation during microsporogenesis in Phaseolus vulgaris L.. Cytol. Genet. 50, 121–127 (2016). https://doi.org/10.3103/S0095452716020109
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3103/S0095452716020109