Abstract
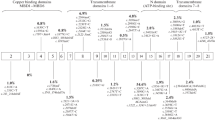
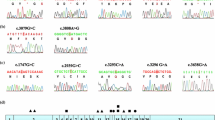
Wilson’s disease (WD) is an autosomal recessive condition caused by an impaired copper metabolism due to hereditary mutations in the ATP7B gene; the spectrum and frequency of mutations are considerably different in different populations. The goal of the study was to determine the most frequent mutations in the ATP7B gene in patients from Ukraine for the introduction of genetic testing into the practice of medical and genetic consulting. The materials for the study were DNA samples isolated from the leukocytes of 90 patients (41 males and 49 females), aged 3–60 with clinical and biochemical signs of the disease. The molecular and genetic analysis of the mutation c.3207C > A (H1069Q), the most common among Europeans, was conducted by the PCR Bi-PASA method. The sequencing of exons of the ATP7B gene was conducted for 23 patients who had a score of three or higher according to the Leipzig scoring system. The molecular and genetic analysis of the mutations in the ATP7B gene genetically verified Wilson’s disease in 23.3% of patients with clinical signs of the disease. Five different mutations and five single-nucleotide polymorphisms in the ATP7B gene were determined in the patients of the investigated group. The mutation c.3207C > A, most common for Europeans, was determined in 28 patients, including 15 cases of homozygosity. In six cases, the mutation c.3207C > A was in a compound heterozygosity state with other mutations in the ATP7B gene: 3–c.2304dupC (8 exon), 1–c.2128G > A (8 exon), 1–c.3011AC (13 exon), 1–c.3402delC (15 exon). No other transformations, except for mutation H1069Q, were found in seven people. The frequency of the pathogenic allele c.3207C > A (H1069Q) of the ATP7B gene, most widespread in Europe, among patients who had a score of three and higher according to the scoring system of diagnostic tests, was 76.8%. The frequency of allele c.2304dupC among genetically verified cases was 7%. The genetic testing of two mutations in the ATP7B gene (c.3207C > A and c.2304dupC), frequent among patients from Ukraine with Wilson’s disease, was introduced into practice. A third of patients did not have pathogenic alleles in exon sequences of the ATP7B gene but had one or several single nucleotide polymorphisms, including several nonpathogenic variants and one polymorphism associated with the increased risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease (c.2495A > G). The obtained results indicate the high informative value from genetic testing of c.3207C > A and c.2304dupC mutations in the ATP7B gene among Ukrainian patients with Wilson’s disease.








Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Bhargava, K., Bahde, R., Kapoor, S., Palestro1, C., and Gupta, S., Evaluation of biliary copper excretion in a rat model of Wilson’s disease by PET imaging with 64Cu-asialofetuin, J. Nucl. Med., 2012, vol. 53, suppl. no. 1.
Langley, A. and Dameron, C.T., Copper and anesthesia: clinical relevance and management of copper related disorders, Anesthesiol. Res. Pract., 2013, vol. 2013, p. 750 901. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/750901
Yu, C.H., Lee, W., Nokhrin, S., and Dmitriev, O.Y., The structure of metal binding domain 1 of the copper transporter ATP7B reveals mechanism of a singular Wilson disease mutation, Sci. Rep., 2018, vol. 12, no. 8, pp. 581–582.
Candan, A., Yaozong, L., and Pernilla, W-S., The six metal binding domains in human copper transporter, ATP7B: molecular biophysics and disease-causing mutations, Biometals, 2017, vol. 30, no. 6, pp. 823–840.
Huster, D., Kühne, A., Bhattacharjee, A., Raines, L., Jantsch, V., Noe, J., Schirrmeister, W., Sommerer, I., Sabri, O., Berr, F., Mössner, J., Stieger, B., Caca, K., and Lutsenko, S., Diverse functional properties of Wilson disease ATP7B variants, Gastroenterology, 2012, vol. 142, no. 4, pp. 947–956.
Shanmugavel, K.P. and Wittung-Stafshede P., Copper relay path through the N-terminus of Wilson disease protein, ATP7B, Metallomics, 2019, vol. 11, pp. 1472– 1480.
Yu, C.H., Yang, N., Bothe, J., Tonelli, M., Nokhrin, S., Dolgova, N.V., Braiterman, L., Lutsenko, S., and Dmitriev, O.Y., The metal chaperone Atox1 regulates the activity of the human copper transporter ATP7B by modulating domain dynamics, J. Biol. Chem., 2017, vol. 292, no. 44, pp. 18 169–18 177.
Hatori, Y. and Lutsenko, S., The role of copper chaperone atox1 in coupling redox homeostasis to intracellular copper distribution, Antioxidants (Basel), 2016, vol. 5, no. 3, p. 25.
Polishchuk, R.S. and Polishchuk, E.V., From and to the Golgi: defining the Wilson disease protein road map, FEBS Lett., 2019, vol. 593, pp. 2341–50.
Chang, I.J. and Si, H.H., The genetics of Wilson disease, Handb. Clin. Neurol., 2017, vol. 142, pp. 19–34.
Khosravifarsani, M., Shabestani, A. M., Pouramir, M., and Zabihi, E., Effects of Fenton reaction on human serum albumin: an in vitro study, Electron. Physician, 2016 vol. 8, no. 9, pp. 2970–2976.
Zhong, H.-J., Sun, H.-H., Xue, L.-F., McGowan, E.M., and Chen, Y., Differential hepatic features presenting in Wilson disease-associated cirrhosis and hepatitis B-associated cirrhosis, World J. Gastroenterol., 2019, vol. 25, no. 3, pp. 378–387.
Lorincz, M.T., Wilson disease and related copper disorders, Handb. Clin. Neurol., 2018, vol. 147, pp. 279–292.
Weiss, K.H. and Stremmel, W., Clinical considerations for an effective medical therapy in Wilson’s disease, Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci., 2014, vol. 1315, pp. 81–85.
Li, W.J., Chen, C., You, Z.F., Yang, R.M., and Wang, X.P., Current drug managements of Wilson’s disease: from West to East, Curr. Neuropharmacol., 2016, vol. 14, no. 4, pp. 322–325.
Purchase, R., The treatment of Wilson’s disease, a rare genetic disorder of copper metabolism, Sci. Progr., 2013, vol. 96, pp. 19–32.
Tanner, S., Clinical and Translational Perspectives on Wilson disease, ScienceDirect, 2019, pp. 1–11.
Makukh, H., Zastavna, D., and Tyrkus, S.I., UA Patent no. 32 044, 2008, Bull. no. 8.
Polakova H., Katrincsakova B., Minarik G., Ferakova E., Ficek A., Baldovic M., et al., Detection of His1069Gln mutation in Wilson disease by bidirectional PCR amplification of specific alleles (BI-PASA) test, Gen. Physiol. Biophys., 2007, vol. 26, pp. 91–96. https://varnomen.hgvs.org/.
Bucossi, S., Mariani, S., Ventriglia, M., Polimanti, R., Gennarelli, M., and Bonvicini, C., Association between the c. 2495 A > G ATP7B polymorphism and sporadic Alzheimer’s disease, Int. J. Alzheimers Dis., 2011, vol. 2011, ID 973692.
Sauna, Z.E. and Kimchi-Sarfaty, C., Synonymous Mutations as a Cause of Human Genetic Disease, eLS, Wiley, 2013. https://doi.org/10.1002/9780470015902.a0025173
Haiboniuk, I., Spectrum and frequency of mutations in gene ATP7B in different populations and ethnic groups, Bull. LNU, 2019, vol. 80, pp. 3–11.
Gomes, A. and Dedoussis, G.V., Geographic distribution of ATP7B mutations in Wilson disease, Ann. Hum. Biol., 2016, vol. 43, pp. 1–8.
Funding
The study was conducted during the internship of H. Makukh in the molecular genetic laboratory with the financial support of Riga Stradins University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest. The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Statement of compliance with standards of research involving humans as subjects. All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants involved in the study.
Additional information
Translated by V. Mittova
About this article
Cite this article
Makukh, H., Hayboniuk, I., Zarina, A. et al. Mutations in the ATP7B Gene in Ukrainian Patients with High Risk of Wilson’s Disease. Cytol. Genet. 54, 324–332 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3103/S009545272004009X
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3103/S009545272004009X