Abstract
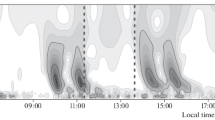
Ionospheric disturbances at an altitude of 300 km that accompanied the solar eclipse of March 20, 2015, have been analyzed based on the ionosondes located in Europe. It has been confirmed that the eclipse was accompanied by the generation of gravity waves in the neutral atmosphere and traveling ionospheric disturbances. The period of the latter was 30–100 min, and the amplitude of relative electron density disturbances was 4–19%. The disturbances continued for not less than 2 h. During the eclipse, the disturbance amplitude more frequently increased. It decreased in one case, since the wave process observed previously was suppressed by the process generated by the eclipse.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
E. L. Afraimovich, V. V. Vodyannikov, S. V. Voeykov, et al., “Ionospheric effects of the March 29, 2006, solar eclipse over Kazakhstan,” Geomagn. Aeron. 47, 461–469 (2007). https://linkspringercom/article/10.1134%2FS0016793207040068
B. B. Borisov, D. A. Egorov, N. E. Egorov, et al., “A comprehensive experimental study of the ionospheric response to the solar eclipse of March 9, 1997,” Geomagn. Aeron. 40, 359–367 (2000).
E. Gossard and W. Hooke, Waves in Atmosphere (Amsterdam: Elsevier, 1975; Mir, Moscow, 1978).
V. P. Uryadov, A. M. Leonov, A. A. Ponyatov, et al., “Variations in the characteristics of a HF signal over an oblique sounding path during the solar eclipse on August 11, 1999,” Radiophys. Quantum Electron. (Engl. Transl.) 43, 614–618 (2000).
L. F. Chernogor, Physical Effects of Solar Eclipses in Atmosphere and Geospace: Monograph (V.N. Karazin Kharkiv National University, Kharkiv, 2013) [in Russian].
L. F. Chernogor and I. F. Domnin, Physics of Geospace Storms: Monograph (V.N. Karazin Kharkiv National University, Kharkiv, 2013) [in Russian].
J. P. Andeniy, O. A. Oladipo, S. M. Radicella, et al., “Analysis on 29 March 2006 eclipse effect on the ionosphere over Ilorin, Nigeria,” J. Geophys. Res.: Space Phys. 114, A11303 (2009). doi 10.1029/2009JA014416
J. O. Adentiyi, S. M. Radicella, I. A. Sdimula, et al., “Signature of the 29 March 2006 eclipse on the ionosphere over an equatorial station,” J. Geophys. Res.: Space Phys. 112, A06314 (2007). doi 10.1029/2006JA012197
E. L. Afraimovich, I. A. Kosogorov, and O. Lesyuta, “Effects of the August 11, 1999 total solar eclipse as deduced from total electron content measurements at the GPS network,” J. Atmos. Sol.-Terr. Phys. 64, 1933–1941 (2002).
E. L. Afraimovich, K. S. Palamartchouk, N. P. Perevalova, et al., “Ionospheric effects of the solar eclipse of March 9, 1997, as deduced from GPS data,” Geophys. Res. Lett. 25, 465–468 (1998).
G. Chen, Z. Zhao, B. Ning, Z. Deng, G. Yang, C. Znou, M. Yao, S. Li, and N. Li, “Latitudinal dependence of the ionospheric response to solar eclipse of 15 January 2010,” J. Geophys. Res.: Space Phys. 116, A06301 (2011). doi doi 10.1029/2010ja016305
G. Chen, Z. Zhao, G. Yang, C. Zhou, M. Yao, T. Li, S. Huang, and N. Li, “Enhancement and HF Doppler observations of sporadic-E during the solar eclipse of 22 July 2009,” J. Geophys. Res.: Space Phys. 115, A09325 (2010). doi 10.1029/2010JA015530
L. F. Chernogor, “Advanced methods of spectral analysis of quasiperiodic wave-like processes in the ionosphere: Specific features and experimental results,” Geomagn. Aeron. 48, 652–673 (2008).
L. F. Chernogor, “Variations in the amplitude and phase of VLF radiowaves in the ionosphere during the August 1, 2008, solar eclipse,” Geomagn. Aeron. 50, 100–110 (2010).
L. F. Chernogor, “Wave response of the ionosphere to the partial solar eclipse of August 1, 2008,” Geomagn. Aeron. 50, 346–361 (2010).
L. F. Chernogor, “Effects of solar eclipses in the ionosphere: Results of Doppler sounding: 1. Experimental data,” Geomagn. Aeron. 52, 768–778 (2012)
L. F. Chernogor, “Effects of solar eclipses in the ionosphere: Doppler sounding results: 2. Spectral analysis,” Geomagn. Aeron. 52, 779–792 (2012).
L. F. Chernogor, “Physical processes in the middle ionosphere accompanying the solar eclipse of January 4, 2011, in Kharkov,” Geomagn. Aeron. 53, 19–31 (2013).
E. A. Cohen, “The study of the effect of solar eclipses on the ionosphere based on satellite beacon observations,” Radio Sci. 19, 769–777 (1984).
K. P. Garmash, S. G. Leus, and L. F. Chernogor, “Radiophysical effects of the January 4, 2011 solar eclipse as observed in the parameters of obliquely propagating HF signals,” Radio Phys. Radio Astron. 2, 325–337 (2011).
W. H. Eccles, “Effect of the eclipse on wireless telegraphic signals,” Electrician 69, 109–116 (1912).
J. V. Evans, “An F region eclipse,” J. Geophys. Res. 70, 131–142 (1965).
T. Farges, J. C. Jodogne, R. Bamford, et al., “Disturbances of the western European ionosphere during the total solar eclipse of 11 August 1999 measured by a wide ionosonde and radar network,” J. Atmos. Sol.-Terr. Phys. 63, 915–924 (2001).
C. R. Huang, C. H. Liu, K. C. Yeh, et al., “A study of tomographically reconstructed ionospheric images during a solar eclipse,” J. Geophys. Res.: Space Phys. 104, 79–94 (1999).
A. N. Hunter, B. K. Holman, D. G. Fieldgate, and R. Kelleher, “Faraday rotation studies in Africa during the solar eclipse of June 30, 1973,” Nature 250, 205–206 (1974).
N. Jakowski, S. M. Stankov, V. Wilken, et al., “Ionospheric behavior over Europe during the solar eclipse of 3 October 2005,” J. Atmos. Sol.-Terr. Phys. 70, 836–853 (2008). doi 10.1016/jjastp.2007.02.016
J. A. Klobuchar and H. E. Whitney, “Ionospheric electron content measurements during a solar eclipse,” J. Geophys. Res. 70, 1254–1257 (1965).
H. Le, L. Liu, X. Yue, and W. Wan, “The ionospheric responses to the 11 August 1999 solar eclipse: observations and modeling,” Ann. Geophys. 18, 107–116 (2008).
H. R. Mimno and P. H. Wang, “Continuous Kennelley-Heaviside layer records of a solar eclipse (with suggestions of a corpuscular effect on the Appleton layer),” Proc. Inst. Radio Eng. 21, 529–545 (1933).
W. L. Oliver and S. A. Bowhill, “The F1 region during a solar eclipse,” Radio Sci. 9, 185–195 (1974).
R. W. Schunk and A. Nagy, Ionospheres: Physics, Plasma Physics, and Chemistry (Cambridge Univ. Press, Cambridge, 2000).
A. T. Tomás, H. Lühr, M. Förster, et al., “Observations of the low-latitude solar eclipse on 8 April 2005 by CHAMP,” J. Geophys. Res.: Space Phys, 112, A06303 (2007). doi 10.1029/2006JA012168
H. F. Tsai and J. Y. Liu, “Ionospheric total electron content response to solar eclipses,” J. Geophys. Res.: Space Phys. 104, 12657–12668 (2007).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © L.F. Chernogor, 2016, published in Kinematika i Fizika Nebesnykh Tel, 2016, Vol. 32, No. 4, pp. 60–72.
About this article
Cite this article
Chernogor, L.F. Wave processes in the ionosphere over Europe that accompanied the solar eclipse of March 20, 2015. Kinemat. Phys. Celest. Bodies 32, 196–206 (2016). https://doi.org/10.3103/S0884591316040024
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3103/S0884591316040024