Abstract
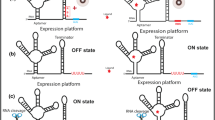
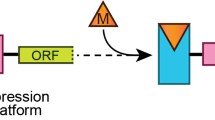
Since last two decades, the role of structural fluctuations of RNA molecules have emerged as one of the key aspects for gene expression in bacteria and they have been found to play very crucial roles for survival of bacteria under highly fluctuating environmental conditions. Riboswitches are one of the RNA elements located in the 5′ region of bacterial mRNA controlling the expression of a gene located downstream to it, by conformational changes of its own upon selective binding to ligands. These molecular fossils are probably the most ancient regulatory system for gene expression. Association of riboswitches with bacterial pathogenesis and other related functions has attracted their exploitation as potential drug targets. Natural as well as synthetic riboswitches hold considerable potential to be the next generation gene control systems to be used in the field of molecular biology and genetic engineering.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Garst, A.D. and Batey, R.D., A switch in time: detailing the life of a riboswitch, Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 2009, vol. 1789, nos. 9–10, pp. 584–591.
Sorek, R., Kunin, V., and Hugenholtz, P., CRISPR—a widespread system that provides acquired resistance against phages in bacteria and archaea, Nat. Rev. Microbiol., 2008, vol. 6, pp. 181–186.
Waters, L.S. and Storz, G., Regulatory RNAs in bacteria, Cell, 2009, vol. 136, pp. 615–628.
Winkler, W.C. and Breaker, R.R., Genetic control by metabolite-binding riboswitches, Chem. Biochem., 2003, vol. 4, pp. 1024–1032.
Nudler, E. and Mironov, A.S., The riboswitch control of bacterial metabolism, Trends. Biochem. Sci., 2004, vol. 29, pp. 11–17.
Tucker, B.J. and Breaker, R., Riboswitches as versatile gene control elements, Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol., 2005, vol. 15, pp. 342–348.
Winkler, W.C., Riboswitches and the role of non-coding RNAs in bacterial metabolic control, Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol., 2005, vol. 9, pp. 594–602.
Barrick, J.E. and Breaker, R., The distributions, mechanisms and structures of metabolite binding riboswitches, Genome Biol., 2007, vol. 8, pp. 11–19.
Rodionov, D.A., Mironov, A.A., and Gelfand, M.S., Conservation of the biotin regulon and the BirA regulatory signal in eubacteria and archaea, Genome Res., 2002, vol. 12, pp. 1507–1516.
Rodionov, D.A., Vitreschak, A.G., Mironov, A.A., and Gelfand, M.S., Comparative genomics of the vitamin B12 metabolism and regulation in prokaryotes, J. Biol. Chem., 2003, vol. 278, pp. 41148–41159.
White, H.B., Coenzymes as fossils of an earlier metabolic state, J. Mol. Evol., 1976, vol. 7, pp. 101–104.
Yin, J.Q. and Wan, Y., RNA-mediated gene regulation system: now and the future, Int. J. Mol. Med., 2012, vol. 10, pp. 355–365.
Lioliou, E., Romilly, C., Romby, P., and Fechter, P., RNA-mediated regulation in bacteria: from natural to artificial systems, Biotechnol. Annu. Rev., 2010, vol. 27, pp. 222–235.
Hiz, M.M. and Aki, C., Gene regulation control by RNA, Ann. Biol. Res., 2012, vol. 3, pp. 5119–5126.
Costa, M. and Michel, F., Frequent use of the same tertiary motif by self-folding RNAs, EMBO J., 1995, vol. 14, pp. 1276–1285.
Cate, J.H., Gooding, A.R., Podell, E., Zhou, K., Golden, B.L., Kundrot, C.E., Cech, T.R., and Doudna, J.A., Crystal structure of a group I ribozyme domain: principles of RNA packing, Science, 1996, vol. 273, pp. 1678–1685.
Williamson, J.R., Induced fit in RNA-protein recognition, Nature. Struct. Biol., 2000, vol. 7, pp. 834–837.
Tuerk, C. and Gold, L., Systematic evolution of ligands by exponential enrichment RNA ligands to bacteriophage T4 DNA polymerase, Science, 1990, vol. 149, pp. 505–510.
Robertson, D.L. and Joyce, G.F., Selection in vitro of an RNA enzyme that specifically cleaves single stranded DNA, Nature, 1990, vol. 344, pp. 467–468.
Ellington, A.D. and Szostak, J.W., In vitro selection of RNA molecules that bind specific ligands, Nature, 1990, vol. 346, pp. 818–822.
Soukup, G.A. and Breaker, R.R., Engineering precision RNA molecular switches, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 1999, vol. 96, pp. 3584–3589.
Soukup, G.A. and Breaker, R.R., Allosteric nucleic acid catalysts, Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol., 2000, vol. 10, pp. 318–325.
Lundrigan, M.D., Koster, W., and Kadner, R.J., Transcribed sequences of the Escherichia coli btuB gene control its expression and regulation by vitamin B12, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 1991, vol. 88, pp. 1479–1483.
Nou, X. and Kadner, R.J., Adenosylcobalamin inhibits ribosome binding to btuB RNA, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 2000, vol. 97, pp. 7190–7195.
Mironov, A.S., Gusarov, I., Rafikov, R., Lopez, L.E., Shatalin, K., Kreneva, R.A., Perumov, D.A., and Nudler, E., Sensing small molecules by nascent RNA: a mechanism to control transcription in Bacteria, Cell, 2002, vol. 111, pp. 747–756.
Regulski and Breaker, R., In-line probing analysis of riboswitches, in Post-Transcriptional Gene Regulation Methods in Molecular Biology, Wilusz, J., Ed., Humana Press, 2008, vol. 419, pp. 53–67.
Winkler, W.C. and Breaker, R., Regulation of bacterial gene expression by riboswitches, Annu. Rev. Microbiol., 2005, vol. 59, pp. 487–517.
Breaker, R., Complex riboswitches, Science, 2008, vol. 319, pp. 1795–1797.
Breaker, R., Riboswitches and the RNA World, Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol., 2012, vol. 4, p. 003566.
Carona, M., Basteta, L., Lussiera, A., Simoneau-Roya, M., Masséb, M., and Lafontaine, D.A., Dualacting riboswitch control of translation initiation and mRNA decay, Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci U.S.A., 2012, vol. 109, pp. 3444–3453.
Fauzia, H., Agyeman, A., and Hinesa, J.V., T box transcription antitermination riboswitch: Influence of nucleotide sequence and orientation on tRNA binding by the antiterminator element, Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 2009, vol. 1789, pp. 185–191.
Garst, A.D., Heroux, A., Rambo, R.P., and Batey, R.T., Crystal structure of the lysine riboswitch regulatory mRNA element, J. Biol. Chem., 2008, vol. 283, pp. 22347–22351.
Draper, D.E., Grilley, D., and Soto, A.M., Ions and RNA folding, Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biomol. Struct., 2005, vol. 34, pp. 221–243.
Woodson, S.A., Metal ions and RNA folding: a highly charged topic with a dynamic future, Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol., 2005, vol. 9, pp. 104–109.
Serganov, A., Huang, L., and Patel, D.J., Structural insights into amino acid binding and gene control by a lysine riboswitch, Nature, 2008, vol. 455, pp. 1263–1267.
Lang, K., Rieder, R., Micura, R., Ligand-induced folding of the thiM TPP riboswitch investigated by a structure-based fluorescence spectroscopic approach, Nucleic Acids Res., 2007, vol. 35, pp. 5370–5378.
Montange, R.K. and Batey, R.T., Structure of the S-adenosylmethionine riboswitch regulatory mRNA element, Nature, 2006, vol. 441, pp. 1172–1175.
Thore, S., Leibundgut, M., and Ban, N., Structure of the eukaryotic thiamine pyrophosphate riboswitch with its regulatory ligand, Science, 2006, vol. 312, pp. 1208–1211.
Serganov, A., Polonskaia, A., Phan, A.T., Breaker, R.R., and Patel, D.J., Structural basis for gene regulation by a thiamine pyrophosphate-sensing riboswitch, Nature, 2006, vol. 441, pp. 1167–1171.
Klein, D.J., and Ferre-D’Amare, A.R., Structural Basis of glmS ribozyme activation by glucosamine-6-phosphate, Science, 2006, vol. 313, pp. 1752–1756.
Cochrane, J.C., Lipchock, S.V., and Strobel, S.A., Structural investigation of the glmS ribozyme bound to its catalytic cofactor, Chem. Biol., 2007, vol. 14, pp. 97–105.
Batey, R.T., Gilbert, S.D., and Montange, R.K., Structure of a natural guanine-responsive riboswitch complexed with the metabolite hypoxanthine, Nature, 2004, vol. 432, pp. 411–415.
Serganov, A., Yuan, Y.R., Pikovskaya, O., Malinina, L., Phan, A.T., Hobartner, C., Micura, R., Breaker, R.R., and Patel, D.J., Structural basis for discriminative regulation of gene expression by adenine- and guaninesensing mRNAs, Chem. Biol., 2004, vol. 11, pp. 1729–1741.
Edwards, T.E. and Ferre-D’Amare, A.R., Crystal structures of the Thi-box riboswitch bound to thiamine pyrophosphate analogs reveal adaptive RNA-small molecule recognition, Structure, 2006, vol. 14, pp. 1459–1468.
Nissen, P., Ippolito, J.A., Ban, N., Moore, P.B., and Steitz, T.A., RNA tertiary interactions to the large ribosomal subunit: the A-minor motif, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 2001, vol. 98, pp. 4899–4903.
Noeske, J., Buck, J., Furtig, B., Nasiri, H.R., Schawalbe, H., and Wohnert, J., Interplay of ‘induced fit’ and preorganization in the ligand induced folding of the aptamer domain of the guanine binding riboswitch, Nucleic Acids Res., 2007, vol. 35, pp. 572–583.
Collins, J.A., Irnov, I., Baker, S., and Winkler, W.C., Mechanism of mRNA destabilization by the glmS ribozyme, Genes Dev., 2007, vol. 24, pp. 3356–3368.
Winkler, W.C., Nahvi, A., Roth, A., Collins, J.A., and Breaker, R.R., Control of gene expression by a natural metabolite-responsive ribozyme, Nature, 2004, vol. 428, pp. 281–286.
Lee, E.R., Baker, J.L., Weinberg, Z., Sudarsan, N., and Breaker, R.R., An allosteric self-splicing ribozyme triggered by a bacterial second messenger, Science, 2010, vol. 329, pp. 845–848.
Chen, A.G.Y., Sudarsan, N., and Breaker, R., Mechanism for gene control by a natural allosteric group I ribozyme, RNA, 2011, vol. 17, pp. 1967–1972.
Mandal, M. and Breaker, R., Adenine riboswitches and gene activation by disruption of a transcription terminator, Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol., 2004, vol. 11, pp. 29–35.
Winkler, W.C., Cohen-Chalamish, S., and Breaker, R., An mRNA structure that controls gene expression by binding FMN, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 2002, vol. 99, pp. 15908–15913.
McDaniel, B.A., Grundy, F.J., Artsimovitch, I., and Henkin, T.M., Transcription termination control of the S box system: direct measurement of S-adenosylmethionine by the leader RNA, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 2003, vol. 100, pp. 3083–3088.
Mandal, M., Boese, B., Barrick, J.E., Winkler, W.C., and Breaker, R.R., Riboswitches control fundamental biochemical pathways in Bacillus subtilis and other bacteria, Cell, 2003, vol. 113, pp. 577–586.
Vitreschak, A.G., Rodionov, D.A., Mironov, A.A., and Gelfand, M.S., Regulation of riboflavin biosynthesis and transport genes in bacteria by transcriptional and translational attenuation, Nucleic Acids Res., 2002, vol. 30, pp. 3141–3151.
Roth, A. and Breaker, R.R., The structural and functional diversity of metabolite binding, Annu. Rev. Biochem., 2009, vol. 78, pp. 305–334.
Ciampi, M.S., Rho-dependent terminators and transcription termination, Microbiology, 2006, vol. 152, pp. 2515–2528.
Winkler, W.C., Nahvi, A., and Breaker, R.R., Thiamine derivatives bind messenger RNAs directly to regulate bacterial gene expression, Nature, 2002, vol. 419, pp. 952–956.
Barrick, J.E., Corbino, K.A., Winkler, W.C., Nahvi, A., Mandal, M., Collins, J., Lee, M., Roth, A., Sudarsan, N., Jona, I., Wickiser, J.K., and Breaker, R.R., New motifs suggest an expanded scope for riboswitches in bacterial genetic control, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 2004, vol. 101, pp. 6421–6426.
Nahvi, A., Sudarsan, N., Evert, M.S., Zou, X., Brown, K.L., and Breaker, R.R., Genetic control by a metabolite binding mRNA, Chem. Biol., 2002, vol. 9, pp. 1043–1049.
Epshtein, V., Mironov, A.S., and Nudler, E., The riboswitch-mediated control of sulfur metabolism in bacteria, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 2003, vol. 100, pp. 5052–5056.
Winkler, W.C., Nahvi, A., Sudarsan, N., Barrick, J.E., and Breaker, R.R., An mRNA structure that controls gene expression by binding S-adenosylmethionine, Nat. Struct. Biol., 2003, vol. 10, pp. 701–707.
Grundy, F.J., Lehman, S.C., and Henkin, T.M., The L box regulon: lysine sensing by leader RNAs of bacterial lysine biosynthesis genes, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 2003, vol. 100, pp. 12057–12062.
Sudarsan, N., Wickiser, J.K., Nakamura, S., Evert, M.S., and Breaker, R.R., An mRNA structure in bacteria that controls gene expression by binding lysine, Genes Dev., 2003, vol. 17, pp. 2688–2697.
Mandal, M., Lee, M., Barrick, J.E., Weinberg, Z., Emillson, G.M., Ruzzo, W.L., and Breaker, R., A Glycine dependent riboswitch that uses cooperative binding to control gene expression, Science, 2004, vol. 306, pp. 275–279.
Dixon, N., Duncan, J.N., Geerlings, T., Dunstan, M.S., McCarthy, J.E.G., Leys, D., and Micklefield, J., Reengineering orthogonally selected riboswitches, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 2010, vol. 107, pp. 2830–2835.
Tang, J. and Breaker, R., Rational design of allosteric ribozymes, Chem. Biol., 1997, vol. 4, pp. 453–459.
Winkler, W.C. and Breaker, R.R., Regulation of bacterial gene expression by riboswitches, Annu. Rev. Microbiol., 2005, vol. 59, pp. 487–517.
Verhouning, A., Karcher, D., and Bock, R., Inducible gene expression from the plastid genome by a synthetic riboswitch, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 2010, vol. 107, pp. 6204–6209.
Thompson, K.M., Syrett, H.A., Knudsen, S.M., and Ellington, A.D., Group I aptazymes as genetic regulatory switches, BMC Biotechnol., 2002, vol. 2, p. 21.
Yen, L., Svendsen, J., Lee, J.S., Gray, J.T., Magnier, M., D’Amato, R.J., and Mulligan, R.C., Exogenous control of mammalian gene expression through modulation of RNA self-cleavage, Nature, 2004, vol. 431, pp. 471–476.
Mulhbacher, J. and Lafontaine, D., Ligand recognition determinants of guanine riboswitches, Nucleic Acids Res., 2007, vol. 35, pp. 5568–5580.
Ott, E., Stolz, J., Lehmann, M., and Mack, M., The RFN riboswitch of Bacillus subtilis is a target for the antibiotic roseoflavin produced by Streptomyces davawensis, RNA Biol., 2009, vol. 6, pp. 276–280.
Serganov, A., Huang, L., and Patel, D.J., Coenzyme recognition and gene regulation by a flavin mononucleotide riboswitch, Nature, 2009, vol. 458, pp. 233–237.
Gerdeman, M.S., Henkin, T.M., and Hines, J.V., Solution structure of the Bacillus subtilis T-box antiterminator RNA: seven nucleotide bulge characterized by stacking and flexibility, J. Mol. Biol., 2003, vol. 326, pp. 189–201.
Durbin, R., Eddy, S.R., Krogh, A., and Mitchison, G., Biological Sequence Analysis, Ch. 10.3: Covariance models: SCFG-Based RNA Profiles, Cambridge University Press, 1998.
Eddy, S.R., A memory-efficient dynamic programming algorithm for optimal alignment of a sequence to an RNA secondary structure, BMC Bioinformatics, 2002, vol. 3, p. 18.
Singh, P., Bandyopadhyay, P., Bhattacharya, S., Krishnamachari, A., and Sengupta, S., Riboswitch Detection Using Profile Hidden Markov Models, BMC Bioinformatics, 2009, vol. 10, pp. 1–13.
Corbino, K.A., Barrick, J.E., Lim, J., Welz, R., Tucker, B.J., Puskarz, I., Mandal, M., Rudnick, N.D., and Breaker, R.R., Evidence for a second class of S-adenosylmethionine riboswitches and other regulatory RNA motifs in alphaproteobacteria, Genome Biol., 2005, vol. 6, p. 70.
Wang, J.X., Lee, E.R., Morales, D.R., Lim, J., and Breaker, R.R., Riboswitchers that sense S-adenosylhomocysteine and activate genes involved in coenzyme recycling, Mol. Cell., 2008, vol. 29, pp. 691–702.
Roth, A., Winkler, W.C., Regulski, E.E., Lee, B.W.K., Lim, J., Jona, I., Barrick, J.E., Ritwik, A., Kim, J.N., Welz, R., Iwata-Reuyl, D., and Breaker, R.R., A riboswitchers selective for the queuosine precursor preQ1 contains an unusually small aptamer domain, Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol., 2007, vol. 14, pp. 308–312.
Cromie, M.J., Shi, Y., Latifi, T., and Groisman, E.A., An RNA sensor for intracellular Mg2+, Cell, 2006, vol. 125, pp. 71–84.
Sudarsan, N., Lee, E.R., Weinberg, Z., Moy, R.H., Kim, J.N., Link, K.H., and Breaker, R.R., Riboswitches in eubacteria sense the second messenger cyclic di-GMP, Science, 2008, vol. 321, pp. 411–413.
Bengert, P. and Dandekar, T., Riboswitch finder—a tool for identification of riboswitch RNAs, Nucleic Acids Res., 2004, vol. 32, pp. 154–159.
Abreu-Goodger, C. and Merino, E., RibEx: a web server for locating riboswitches and other conserved bacterial regulatory elements, Nucleic Acids Res., 2005, vol. 33, pp. 690–692.
Chang, T.H., Wu, L.C., Yeh, C.T., Liu, B.J., Huang, H.D., and Horng, J.T., Computational Identification of riboswitches based on RNA conserved functional sequences and conformations, RNA, 2009, vol. 15, pp. 1426–1430.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The article is published in the original.
About this article
Cite this article
Ray, S., Chakdar, H. Riboswitch: Ancient living switch for gene regulation. Mol. Genet. Microbiol. Virol. 29, 227–239 (2014). https://doi.org/10.3103/S0891416814040090
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3103/S0891416814040090