Abstract
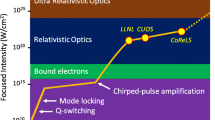
At the Center for Relativistic Laser Science (CoReLS) petawatt (PW) lasers have been developed for the investigations of strong field physics. The CoReLS has successfully upgraded one of the existing PW laser beamlines to a 4 PW laser at 20 fs. From laser-driven charged-particle acceleration experiments, multi-GeV electrons and 90-MeV protons can be generated using the laser wakefield acceleration and the radiation pressure acceleration schemes, respectively. The GeV electron beam can be, in turn, used for Compton backscattering with another PW laser. Such a Compton scattering process can be examined for other quantum electrodynamics (QED) effects, including the radiation reaction effect and the Breit-Wheeler pair production process. PW lasers have, thus, offered new opportunities to pursue novel physics research in relativistic plasma physics, strong field quantum electrodynamics, nuclear physics and laboratory astrophysics.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. V. Korzhimanov, A. A. Gonoskov, E. A. Khazanov and A. M. Sergeev, Phys. Usp. 54, 9 (2011).
National Academy of Sciences, Opportunities in Intense Ultrafast Lasers: Reaching for the Brightest Light (The National Academies Press, Washington, DC, 2018).
G. A. Mourou, T. Tajima and S. V. Bulanov, Rev. Mod. Phys. 78, 309 (2006).
E. Esarey, C. Schroeder and W. Leemans, Rev. Mod. Phys. 81, 1229 (2009).
H. Daido, M. Nishiuchi and A. S. Pirozhkov, Rep. Prog. Phys. 75, 056401 (2012).
A. Macchi, M. Borghesi and M. Passoni, Rev. Mod. Phys. 85, 751 (2013).
J. Schreiber, P. Bolton and K. Parodi, Rev. Sci. Instrum. 87, 071101 (2016).
H. T. Kim et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 111, 165002 (2013).
H. T. Kim et al., Sci. Rep. 7, 10203 (2017).
I. J. Kim et al., Phys. Plasmas 23, 070701 (2016).
A. Di Piazza, C. Müller, K. Hatsagortsyan and C. Keitel, Rev. Mod. Phys. 84, 1177 (2012).
S. Bulanov, T. Z. Esirkepov, M. Kando, J. Koga, K. Kondo and G. Korn, Plasma Phys. Rep. 41, 1 (2015).
P. Gibbon, Short pulse laser interactions with matter (Imperial College Press, London, 2005).
A. Macchi, A Superintense Laser-Plasma Interaction Theory Primer (Springer, Dordrecht, 2013).
F. Albert and A. G. Thomas, Plasma Phys. Controlled Fusion 58, 103001 (2016).
S. Eliezer, The interaction of high-power lasers with plasmas (CRC Press, Bristol, 2002).
U. Teubner and P. Gibbon, Rev. Mod. Phys. 81, 445 (2009).
C. Thaury and F. Quéré, J. Phys. B: At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 43, 213001 (2010).
I. J. Kim et al., Nat. Commun. 3, 1231 (2012).
A. Macchi, A. Sgattoni, S. Sinigardi, M. Borghesi and M. Passoni, Plasma Phys. Controlled Fusion 55, 124020 (2013).
I. J. Kim et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 111, 165003 (2013).
K. H. Pae, C. M. Kim and C. H. Nam, Phys. Plasmas 23, 033117 (2016).
L. Fedeli, High Field Plasmonics (Springer, Dordrecht, 2016).
J. Cole et al., Phys. Rev. X 8, 011020 (2018).
N. Narozhny and A. Fedotov, Contemp. Phys. 56, 249 (2015).
T. Huang et al., arXiv preprint arXiv:1803.08237 (2018).
A. Pukhov, Z-M. Sheng and J. Meyer-ter Vehn, Phys. Plasmas 6, 2847 (1999).
T. Arber et al., Plasma Phys. Controlled Fusion 57, 113001 (2015).
G. Gregori, B. Reville and F. Miniati, Phys. Rep. 601, 1 (2015).
P. Tzeferacos et al., Nat. Commun. 9, 591 (2018).
G. Sarri et al., Nat. Commun. 6, 6747 (2015).
M. Lobet, X. Davoine, E. dHumières and L. Gremillet, Phys. Rev. AB 20, 043401 (2017).
J. Warwick et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 119, 185002 (2017).
D. Strickland and G. Mourou, Opt. Commun. 56, 219 (1985).
M. Perry et al., in CLEO’ 96., Summaries of papers presented at the Conference on Lasers and Electro-Optics (IEEE, 1996), p. 307.
K. Yamakawa, M. Aoyama, S. Matsuoka, T. Kase, Y. Akahane and H. Takuma, Opt. Lett. 23, 1468 (1998).
M. Aoyama et al., Opt. Lett. 28, 1594 (2003).
J. H. Sung, S. K. Lee, T. J. Yu, T. M. Jeong and J. Lee, Opt. Lett. 35, 3021 (2010).
T. J. Yu, S. K. Lee, J. H. Sung, J. W. Yoon, T. M. Jeong and J. Lee, Opt. Express 20, 10807 (2012).
J. H. Sung et al., Opt. Lett. 42, 2058 (2017).
K. Ertel, C. Hooker, S. J. Hawkes, B. T. Parry and J. L. Collier, Opt. Express 16, 8039 (2008).
T. Tajima and J. Dawson, Phys. Rev. Lett. 43, 267 (1979).
A. Pukhov and J. Meyer-ter Vehn, Appl. Phys. B 74, 355 (2002).
X. Wang et al., Nat. Commun. 4, 1988 (2013).
W. Leemans et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 113, 245002 (2014).
V. B. Pathak, H. T. Kim, J. Vieira, L. O. Silva and C. H. Nam, submitted (2018).
M. H. Cho, V. B. Pathak, H. T. Kim and C. H. Nam, submitted (2018).
M. Borghesi et al., Phys. Plasmas 9, 2214 (2002).
K. W. D. Ledingham, P. McKenna and R. P. Singhal, Science 300, 1107 (2003).
T. Tajima, D. Habs and X. Yan, in Reviews of Accelerator Science and Technology.: Volume 2: Medical Applications of Accelerators (World Scientific, Singapore, 2009), p. 201.
S. P. Hatchett et al., Phys. Plasmas 7, 2076 (2000).
L. O. Silva et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 92, 015002 (2004).
S. Bulanov et al., Phys. Rev. E 78, 026412 (2008).
A. Henig et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 103, 245003 (2009).
A. Robinson, M. Zepf, S. Kar, R. Evans and C. Bellei, New J. Phys. 10, 013021 (2008).
I. J. Kim et al., High Energy Density Phys. 17, 203 (2015).
I. W. Choi et al., Appl. Phys. Lett. 99, 181501 (2011).
I. W. Choi et al., Rev. Sci. Instrum. 80, 053302 (2009).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, S.K., Kim, H.T., Choi, I.W. et al. Exploration of Strong Field Physics with Multi-PW Lasers. J. Korean Phys. Soc. 73, 179–189 (2018). https://doi.org/10.3938/jkps.73.179
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3938/jkps.73.179